Effects of Virtual Reality training on medical students' learning motivation and competency
- PMID: 31258607
- PMCID: PMC6572943
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.35.3.44
Effects of Virtual Reality training on medical students' learning motivation and competency
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the need of contemporary immersive approaches (Virtual Reality) in teaching and training at medical sector. The main objective of this study was to explore the effects of text, video and immersive technologies learning methodologies for participants' learning in public and private medical colleges and universities of Pakistan.
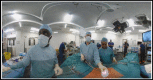
Methods: In this quantitative research 87 medical students of 4th year from three public and five private medical colleges and universities participated. A laparoscopy operation was selected in consultation with senior medical consultants for this experiment. The experimental material was arranged in virtual reality, video and text based learning. At completion of each of which, participants completed a questionnaire about learning motivation and learning competency through the different mediums.
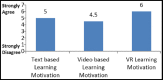
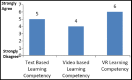
Results: Statistical t-test was selected for the analysis of this study. By comparing the mean values of virtual reality, video, and text based learning methodologies in medical academics; result of virtual reality is at top of others. All performed model are statistically significant (P=0.000) and results can be applied at all population.
Conclusion: Through this research, we contribute to medical students learning methodologies. In medical studies, both theoretical and practical expertise has a vital role, while repetition of hands-on practice can improve young doctors' professional competency. Virtual reality was found best for medical students in both learning motivation and learning competency. Medical students and educationist may select virtual reality as new learning methodology for curriculum learning.
Keywords: Virtual reality (VR); text based learning (TBL); video based learning (VBL).
Figures
References
-
- Zhang S, Zhao J, Tan W. Extending TAM for online learning systems:An intrinsic motivation perspective. Tsinghua Sci Technol. 2008;13(3):312–317.
-
- Psotka J. Immersive training systems:Virtual reality and education and training. Instr Sci. 1995;23(5–6):405–431.
-
- Jibury O Al. Use of Virtual Reality in Medical Education - Reality or Deception. Med Case Rep. 2017;3(01):100039. Available from: http://medical-case-reports.imedpub.com/use-of-virtual-reality-in-medica... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources