Effect of miR-19b on the protective effect of Exendin-4 on islet cells in non-obese diabetic mice
- PMID: 31258687
- PMCID: PMC6566081
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7598
Effect of miR-19b on the protective effect of Exendin-4 on islet cells in non-obese diabetic mice
Abstract
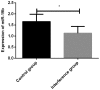
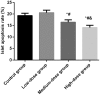
This study analyzed the effect of miR-19b on the protective effect of Exendin-4 on islet cells in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Twenty-four NOD/LT mice were randomized, according to the random number table, into a control group (4 µg/kg•day), a low-dose group (2 µg/kg•day Exendin-4), a medium-dose group (4 µg/kg•day Exendin-4) and a high-dose group (8 µg/kg•day Exendin-4) (n=6), with miR-19b expression interfered (an interference group) except for the control group. RT-qPCR was used to detect interference results and different doses of Exendin-4 were given for 8 weeks of intervention after the interference. CD4+ and CD8+ cell levels were detected by flow cytometry, IL-2 and IL-10 levels in the peripheral blood by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the apoptosis rate of islet cells in the pancreatic tissue by TUNEL. After 4 and 8 weeks of Exendin-4 intervention, mice in the high-dose group had lower blood glucose level than the medium-dose group (P<0.05). The medium-dose group had lower CD4+ cell level than the high-dose group (P<0.05), while the medium-dose group had higher CD8+ cell level than the high-dose group (P<0.05). After 8 weeks of intervention, compared with the medium-dose group, the high-dose group had lower IL-2 level (P<0.05), but higher IL-10 level (P<0.05). After 8 weeks of intervention, the medium-dose group had a higher apoptosis rate than the high-dose group (P<0.05). In conclusion, the decrease in miR-19b expression can improve the therapeutic effect of Exendin-4 on NOD, control blood glucose effectively and improve inflammatory response and immune function, as well as reduce islet cell injury. The increase in the dose of Exendin-4 can further improve its therapeutic effect on NOD.
Keywords: Exendin-4; islet cells; miR-19b; non-obese diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Kendall DM, Riddle MC, Rosenstock J, Zhuang D, Kim DD, Fineman MS, Baron AD. Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control over 30 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin and a sulfonylurea. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1083–1091. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.5.1083. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
