Herpesvirus acts with the cytoskeleton and promotes cancer progression
- PMID: 31258722
- PMCID: PMC6584404
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.30222
Herpesvirus acts with the cytoskeleton and promotes cancer progression
Abstract
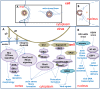
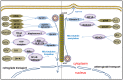
The cytoskeleton is a complex fibrous reticular structure composed of microfilaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments. These components coordinate morphology support and intracellular transport that is involved in a variety of cell activities, such as cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. In addition, the cytoskeleton also plays an important role in viral infection. During an infection by a Herpesvirus, the virus utilizes microfilaments to enter cells and travel to the nucleus by microtubules; the viral DNA replicates with the help of host microfilaments; and the virus particles start assembling with a capsid in the cytoplasm before egress. The cytoskeleton changes in cells infected with Herpesvirus are made to either counteract or obey the virus, thereby promote cell transforming into cancerous ones. This article aims to clarify the interaction between the virus and cytoskeleton components in the process of Herpesvirus infection and the molecular motor, cytoskeleton-associated proteins and drugs that play an important role in the process of a Herpesvirus infection and carcinogenesis process.
Keywords: Herpesvirus; cancer; cytoskeleton; drugs; infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of frog virus-3 with the cytoskeleton. I. Altered organization of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments.J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1248-57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1248. J Cell Biol. 1983. PMID: 6341377 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-herpesvirus infection induces the formation of nuclear actin filaments.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Aug;2(8):e85. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020085. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16933992 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus modulates microtubule dynamics via RhoA-GTP-diaphanous 2 signaling and utilizes the dynein motors to deliver its DNA to the nucleus.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(2):1191-206. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.1191-1206.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15613346 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the cytoskeleton in hormone action.Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;62(8):653-65. doi: 10.1139/o84-087. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984. PMID: 6093963 Review.
-
Role of cytoskeletal motor proteins in viral infection.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 Oct 30;66:810-7. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1016360. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 23175336 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal X chromosome inactivation and tumor development.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Aug;77(15):2949-2958. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03469-z. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32040694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Non-Essential" Proteins of HSV-1 with Essential Roles In Vivo: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2020 Dec 23;13(1):17. doi: 10.3390/v13010017. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33374862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression Network for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:809760. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.809760. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875165 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Dissemination Through Peripheral Nerves Explains Multiple Organ Injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Aug 5;14:229. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00229. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848621 Free PMC article.
-
Equid Alphaherpesvirus 1 Modulates Actin Cytoskeleton and Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Line A172.Pathogens. 2022 Mar 25;11(4):400. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11040400. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35456075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roizman B, Carmichael LE, Deinhardt F. et al. Herpesviridae. Intervirology. 1981;16:201–17. - PubMed
-
- Dang L, Teng M, Li HZ. et al. Marek's disease virus type 1 encoded analog of miR-155 promotes proliferation of chicken embryo fibroblast and DF-1 cells by targeting hnRNPAB. Vet Microbiol. 2017;207:210–8. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Gu B, Zhou F. et al. Human herpesvirus 6A infects human embryonic fibroblasts and induces G2/M arrest and cell death. J Med Virol. 2012;84:657–63. - PubMed
-
- Tu C, Zeng Z, Qi P. et al. Identification of genomic alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived Epstein-Barr virus by whole-genome sequencing. Carcinogenesis. 2018;39:1517–28. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

