Identification of novel methylated DNA marker ZNF569 for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 31258729
- PMCID: PMC6584424
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31156
Identification of novel methylated DNA marker ZNF569 for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
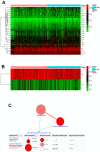
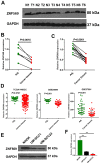
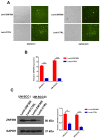
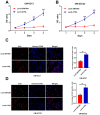
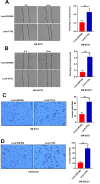
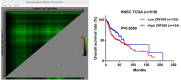
Aberrant DNA methylation pattern plays an indispensable role in the initiation and development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). It is well recognized that lymph node metastasis is closely with unfavorable prognosis of HNSCC. Therefore, exploring the methylation events accounting for the lymph node metastasis of HNSCC is very important for improving the clinical outcome of HNSCC. Methylation data, RNA-seq data and clinical data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and processed using the R package TCGA-Assembler. MethylMix was use for data analysis by integrating both methylation and gene expression data on HNSCC patients with lymph node metastasis and without lymph node metastasis. Pathway analysis was performed on significantly altered genes using ConsensusPathDB. The role of our interested gene zinc figure protein 569 (ZNF569) in HNSCC was further evaluated. Our results identified many novel hypermethylated/hypomethylated genes that might be closely associated with the lymph node metastasis of HNSCC. Pathway analysis revealed that increase in methylation of genes involved in generic transcription pathway including zinc figure proteins. ZNF569 was hypermethylated in HNSCC tissues especially those with lymph node metastasis. In addition, the expression levels of ZNF569 mRNA and protein were significantly lower in HNSCC tissues and cell lines compared to their respective controls. Moreover, overexpression of ZNF569 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of HNSCC cells. HNSCC patients with lower ZNF569 expression suffered a significantly shorter overall survival than those with higher ZNF569 expression. In conclusion, we have identified many novel differentially methylated genes that might be important for the lymph node metastasis of HNSCC. In addition, ZNF569 might play a tumor suppressive role in carcinogenesis of HNSCC.
Keywords: Carcinogenesis; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Methylation; Zinc figure protein 569.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of novel hub genes associated with lymph node metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by completive bioinformatics analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Nov;9(22):1678. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5704. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34988187 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prognostic marker genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database and experimental validation.J Oral Pathol Med. 2021 Oct;50(9):891-901. doi: 10.1111/jop.13186. Epub 2021 May 19. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021. PMID: 33880801
-
TBC1D14 inhibits autophagy to suppress lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating macrophage erythroblast attacher.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb 7;18(5):1795-1812. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68992. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342354 Free PMC article.
-
The Overexpression of NMHC IIA Promoted Invasion and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.J Cancer. 2021 May 17;12(14):4218-4228. doi: 10.7150/jca.47506. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093822 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative review of research progress of RNA m5C methylation in head and neck malignancies.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):5112-5122. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-103. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a m6A RNA methylation regulators-based signature for predicting the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 1;9(10):2156-2169. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31720080 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Prognostic Model for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Functions and Prognostic Values of RNA-Binding Proteins.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 30;11:592614. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.592614. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34395233 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA methylation-based test for esophageal cancer detection.Biomark Res. 2020 Nov 25;8(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00248-7. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 33292587 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic integrative analysis pinpoint master regulator transcription factors associated with tumorigenesis in squamous cell carcinoma of oral tongue.Genet Mol Biol. 2023 Jun 19;46(2):e20220358. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2022-0358. eCollection 2023. Genet Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37338302 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of an alternative splicing-based prognostic signature for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 May 18;11(15):4571-4580. doi: 10.7150/jca.44746. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32489474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–36. - PubMed
-
- Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A, Sidransky D. Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1890–900. - PubMed
-
- Moore LD, Le T, Fan G.DNA methylation, its basic function. Neuropsycho-pharmacology. 2013; 38:23-38.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

