Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and G2/M Phase Arrest through the ERK Pathways in Esophageal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 31258746
- PMCID: PMC6584355
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.32071
Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and G2/M Phase Arrest through the ERK Pathways in Esophageal Cancer Cells
Abstract
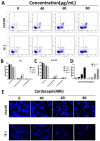
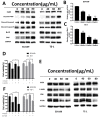
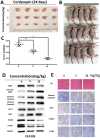
Esophageal cancer is one of the most aggressive and lethal gastrointestinal tract malignancies, with a poor overall five-year survival rate. Cordycepin, a major compound of Cordyceps sinensis, has been shown to have anticancer potential. This study focuses on the anticancer properties of cordycepin that target esophageal cancer and reveals molecular aspects underlying these effects. In our CCK-8 assays and colony formation assays, cordycepin significantly suppressed esophageal cancer cell proliferation. Moreover, cordycepin induced chromatin condensation in esophageal cancer cells and significantly increased the number of apoptotic cells through activation of caspase cascades, apoptotic signaling, and the regulation of Bcl-2 family members. Cell cycle assays showed that cordycepin altered cyclin-dependent kinase1 and cyclinB1 expression, which resulted in a G2/M phase blockade. Mechanistically, ERK pathway inactivation was involved in the anti-tumor functions of cordycepin. The same results were also observed in vivo. Taken together, these findings reveal that cordycepin induces pro-apoptosis and anti-proliferation mechanisms in cancer cells, and may represent a novel therapeutic agent.
Keywords: ERK; apoptosis; cell cycle; cordycepin; esophageal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cordycepin, a Natural Antineoplastic Agent, Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via Caspase-dependent Pathways.Nat Prod Commun. 2016 Jan;11(1):63-8. Nat Prod Commun. 2016. PMID: 26996021
-
Cordycepin induces apoptosis in human liver cancer HepG2 cells through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways.Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):995-1000. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4706. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446383 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo via targeting FGFR2 and blocking ERK signaling.Chin J Nat Med. 2020 May;18(5):345-355. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30041-8. Chin J Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32451092
-
The Anticancer Properties of Cordycepin and Their Underlying Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 4;19(10):3027. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103027. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30287757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer and antimetastatic effects of cordycepin, an active component of Cordyceps sinensis.J Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Jan;127(1):53-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25704018 Review.
Cited by
-
FRA-1 suppresses apoptosis of Helicobacter pylori infected MGC-803 cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):611-621. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06105-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33389529
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 Attenuates Triptolide-Induced Cytotoxicity in HL-7702 Cells via the Activation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:723784. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.723784. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046796 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanisms of cordycepin in inhibiting cancer cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Aug 23;57:e13889. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13889. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39194034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and pharmacological insights into cordycepin for neoplasms and metabolic disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 17;15:1367820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1367820. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38953102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cordycepin mitigates spermatogenic and redox related expression in H2O2-exposed Leydig cells and regulates testicular oxidative apoptotic signalling in aged rats.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):404-416. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2033275. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35175170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi AK, El-Serag HB. Esophageal carcinoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2014;371:2499–509. - PubMed
-
- Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature. 2005;438:946–53. - PubMed
-
- Hsu WH, Hsu PK, Hsieh CC, Huang CS, Wu YC. The metastatic lymph node number and ratio are independent prognostic factors in esophageal cancer. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery: official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 2009;13:1913–20. - PubMed
-
- Cassileth BR. Alternative and Complementary Cancer Treatments. The oncologist. 1996;1:173–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

