Dysregulation of MiR-519d Affects Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis by Targeting MMP3
- PMID: 31258780
- PMCID: PMC6584932
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31825
Dysregulation of MiR-519d Affects Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis by Targeting MMP3
Abstract
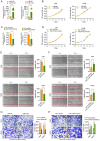
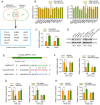
MicroRNA-519d (miR-519d) has been reported to play important roles in tumor development and progression in multiple cancers, either as tumor suppressor or tumor promotor. However, the expression level, biological function and molecular mechanisms of miR-519d in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remain unclear. Therefore, the aims of this study were to investigate the functional role of miR-519d in OSCC and the possible underlying regulatory mechanism. In this study, we found that miR-519d was significantly downregulated in OSCC tissues and cell lines compared with normal oral mucosae and normal oral epithelial cells. Importantly, downregulation of miR-519d was closely correlated with the lymph node metastasis, advanced tumor stage and poor overall survival of OSCC patients. Furthermore, miR-519d significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of OSCC cells. Using bioinformatics and biological approaches, we showed that miR-519d directly targeted matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3), which might account for the underlying mechanism involved in the miR-519d mediated suppression of OSCC progression. What is more, miR-519d expression was inversely correlated with MMP3 expression in OSCC tissues, and high levels of MMP3 expression in OSCC tissues were also associated with the metastasis and poor prognosis of these patients. In addition, we further identified that miR-519d acted as a regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in OSCC cells. Overall, the present study highlighted miR-519d as a tumor suppressor in OSCC by targeting MMP3 and supported biological and clinical links between miR-519d-MMP3 and OSCC, thus indicating the potential therapeutic value of miR-519d for alleviating OSCC metastasis.
Keywords: MMP3; epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); invasion; metastasis; miR-519d; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-519d suppresses breast cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis via targeting MMP3.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Feb 9;14(2):228-236. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.22849. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483840 Free PMC article.
-
MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Aug 15;9(8):3654-3664. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28861156 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-101 inhibits oral squamous-cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 1;6(6):1396-407. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27429852 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An insight into molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020 Jan-Apr;24(1):189. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_334_19. Epub 2020 May 8. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32508481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of long noncoding RNAs as regulators of the epithelial-Mesenchymal transition process in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 29;9:942636. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.942636. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36106022 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
circ_0007385 served as competing endogenous RNA for miR-519d-3p to suppress malignant behaviors and cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Aug;11(8):2196-2208. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13527. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32602212 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of potential novel biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8845-8862. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1987089. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34606406 Free PMC article.
-
The integration of differentially expressed genes based on multiple microarray datasets for prediction of the prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3309-3321. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1947076. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34224327 Free PMC article.
-
New stem cell autophagy surrogate diagnostic biomarkers in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in Egypt: A pilot study.World J Hepatol. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):2137-2149. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.2137. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 35070014 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Investigation of Chemotherapeutic Resistance and miRNA Expressions in Head and Neck Cancers: A Thorough PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;13(12):2325. doi: 10.3390/genes13122325. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Mao L. Oral squamous cell carcinoma - progresses from risk assessment to treatment. Chin J Dent Res. 2012;15:83–8. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

