Neuroendocrine Regulation of Brain Cytokines After Psychological Stress
- PMID: 31259292
- PMCID: PMC6595533
- DOI: 10.1210/js.2019-00053
Neuroendocrine Regulation of Brain Cytokines After Psychological Stress
Abstract
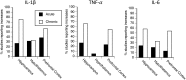
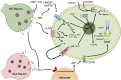
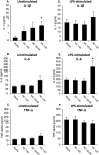
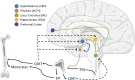
There is growing evidence that stress-induced brain cytokines are important in the etiology of depression and anxiety. Here, we review how the neuroendocrine responses to psychological stressors affect the immediate and long-term regulation of inflammatory cytokines within the brain and highlight how the regulation changes across time with repeated stress exposure. In doing so, we report on the percentage of studies in the literature that observed increases in either IL-1β, TNF-α, or IL-6 within the hypothalamus, hippocampus, or prefrontal cortex after either acute or chronic stress exposure. The key takeaway is that catecholamines and glucocorticoids play critical roles in the regulation of brain cytokines after psychological stress exposure. Central catecholamines stimulate the release of IL-1β from microglia, which is a key factor in the further activation of microglia and recruitment of monocytes into the brain. Meanwhile, the acute elevation of glucocorticoids inhibits the production of brain cytokines via two mechanisms: the suppression of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons and inhibition of the NFκB signaling pathway. However, glucocorticoids and peripheral catecholamines facilitate inflammatory responses to future stimuli by stimulating monocytes to leave the bone marrow, downregulating inhibitory receptors on microglia, and priming inflammatory responses mediated by peripheral monocytes or macrophages. The activation of microglia and the elevation of peripheral glucocorticoid and catecholamine levels are both necessary during times of stress exposure for the development of psychopathologies.
Keywords: IL-1β; IL-6; TNF-α; hippocampus; hypothalamus; prefrontal cortex.
Figures
References
-
- Kessler RC. The effects of stressful life events on depression. Annu Rev Psychol. 1997;48(1):191–214. - PubMed
-
- Levine J, Barak Y, Chengappa KN, Rapoport A, Rebey M, Barak V. Cerebrospinal cytokine levels in patients with acute depression. Neuropsychobiology. 1999;40(4):171–176. - PubMed
-
- Köhler CA, Freitas TH, Stubbs B, Maes M, Solmi M, Veronese N, de Andrade NQ, Morris G, Fernandes BS, Brunoni AR, Herrmann N, Raison CL, Miller BJ, Lanctôt KL, Carvalho AF. Peripheral alterations in cytokine and chemokine levels after antidepressant drug treatment for major depressive disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(5):4195–4206. - PubMed
-
- Maes M. Evidence for an immune response in major depression: a review and hypothesis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1995;19(1):11–38. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
