Platelet Activation Is Limited during Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients on Aspirin Monotherapy and without per Procedural Clinical Complications
- PMID: 31259296
- PMCID: PMC6598084
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1692142
Platelet Activation Is Limited during Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients on Aspirin Monotherapy and without per Procedural Clinical Complications
Abstract
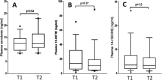
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is an established treatment option for symptomatic patients with severe aortic valve stenosis (AS). During and early after the procedure, both ischemic events (predominantly stroke) and bleedings remain prevalent. The optimal antithrombotic regimen is still debated. Single- versus dual-antiplatelet therapy is associated with a lower rate of severe bleeding, without difference in thrombotic complications. Although platelets have been empirically targeted, little is known on their contribution to these events primarily related to embolization of thrombotic material and tissue-derived debris from the wounded aortic valve and large vessels. The objective of this study was to assess local platelet activation in blood sampled in the ascending aorta immediately before and within minutes postimplantation. A series of 18 patients with AS on monotherapy with aspirin successfully underwent TAVI with the self-expandable Medtronic CoreValve by transfemoral route. No clinical thrombotic complication occurred at 30-day follow-up. Compared with patients with stable coronary artery disease unscathed of AS and similarly treated by low-dose aspirin, AS patients displayed a chronic state of platelet activation before TAVI, assessed in venous blood using various biomarkers. However, per procedure, in aortic blood, no change occurred between the two time points in the plasma levels of serotonin or 12-lipoxgenase products, or membrane exposure of granule markers CD62-P and CD63. Our results suggest that local acute platelet activation is limited during TAVI on monotherapy with aspirin.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; platelet activation; transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspirin Versus Aspirin Plus Clopidogrel as Antithrombotic Treatment Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With a Balloon-Expandable Valve: The ARTE (Aspirin Versus Aspirin + Clopidogrel Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) Randomized Clinical Trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 Jul 10;10(13):1357-1365. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.04.014. Epub 2017 May 17. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017. PMID: 28527771 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimalistic Approach for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI): Open Vascular Vs. Fully Percutaneous Approach.Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2019 Oct 1;40(2):5-14. doi: 10.2478/prilozi-2019-0009. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2019. PMID: 31605589
-
The role of platelet reactivity assessment in dual antiplatelet prophylaxis after transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018 Apr;111(4):233-245. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29126843
-
Antithrombotic treatment in transcatheter aortic valve implantation: insights for cerebrovascular and bleeding events.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Dec 24;62(25):2349-2359. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.03.029. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23583252 Review.
-
Antithrombotic treatment in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI).Thromb Haemost. 2015 Apr;113(4):674-85. doi: 10.1160/TH14-10-0821. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25653053 Review.
References
-
- Nijenhuis V J, Bennaghmouch N, van Kuijk J P, Capodanno D, ten Berg J M. Antithrombotic treatment in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(04):674–685. - PubMed
-
- Puri R, Altisent O A, Campelo-Parada F, del Trigo M, Regueiro A, Rodés-Cabau J. Balancing the risks of thrombosis and bleeding following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: current state-of-evidence. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(13):1904–1910. - PubMed
-
- Erdoes G, Basciani R, Huber Cet al.Transcranial Doppler-detected cerebral embolic load during transcatheter aortic valve implantation Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 20124104778–783., discussion 783–784 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous