Klebsiella variicola: an emerging pathogen in humans
- PMID: 31259664
- PMCID: PMC6609320
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1634981
Klebsiella variicola: an emerging pathogen in humans
Abstract
The Klebsiella pneumoniae complex comprises seven K. pneumoniae-related species, including K. variicola. K. variicola is a versatile bacterium capable of colonizing different hosts such as plants, humans, insects and animals. Currently, K. variicola is gaining recognition as a cause of several human infections; nevertheless, its virulence profile is not fully characterized. The clinical significance of K. variicola infection is hidden by imprecise detection methods that underestimate its real prevalence; however, several methods have been developed to correctly identify this species. Recent studies of carbapenemase-producing and colistin-resistant strains demonstrate a potential reservoir of multidrug-resistant genes. This finding presents an imminent scenario for spreading antimicrobial resistant genes among close relatives and, more concerningly, in clinical and environmental settings. Since K. variicola was identified as a novel bacterial species, different research groups have contributed findings elucidating this pathogen; however, important details about its epidemiology, pathogenesis and ecology are still missing. This review highlights the most significant aspects of K. variicola, discussing its different phenotypes, mechanisms of resistance, and virulence traits, as well as the types of infections associated with this pathogen.
Keywords: Nitrogen fixation; bacterial infections; misclassification; molecular epidemiology; multidrug-resistant.
Figures
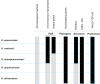
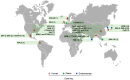
References
-
- Brisse S, Passet V, Grimont PA.. Description of Klebsiella quasipneumoniae sp. nov., isolated from human infections, with two subspecies, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae subsp. nov. and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae subsp. nov., and demonstration that Klebsiella singaporensis is a junior heterotypic synonym of Klebsiella variicola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014;64:3146–3152. - PubMed
-
- Brisse S, Verhoef J.. Phylogenetic diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca clinical isolates revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA, gyrA and parC genes sequencing and automated ribotyping. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:915–924. - PubMed
-
- Rosenblueth M, Martinez L, Silva J, et al. Klebsiella variicola, a novel species with clinical and plant-associated isolates. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2004;27:27–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
