Increasing severity of atopic dermatitis is associated with a negative impact on work productivity among adults with atopic dermatitis in France, Germany, the U.K. and the U.S.A
- PMID: 31260080
- PMCID: PMC7187138
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.18296
Increasing severity of atopic dermatitis is associated with a negative impact on work productivity among adults with atopic dermatitis in France, Germany, the U.K. and the U.S.A
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with high disease burden, with a significant physical and social impact. However, the association between disease severity and burden of disease, with work productivity and daily activities being one aspect, has not been well characterized.
Objectives: To investigate the impact of disease severity on work productivity and daily activities among adults with AD in Europe (France, Germany and the U.K.) and the U.S.A.
Methods: The survey panel participants for this cross-sectional internet-based survey on AD were sourced from the population-based National Health and Wellness Survey (Europe 2016, U.S.A. 2015 and 2016). AD severity was determined by Patient-Oriented Scoring Atopic Dermatitis (PO-SCORAD). Work productivity and work activity impairment were assessed using the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) - Specific Health Problem questionnaire for AD.
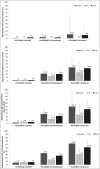
Results: The study survey was completed by 1098 respondents with moderate-to-severe AD and 134 with mild AD. Overall, the negative impact on work productivity (all WPAI items) was suggested to increase with increasing AD severity (PO-SCORAD) at the regional level (Europe and U.S.A.) and in the total sample. For overall work impairment due to AD, respondents with mild AD reported a mean of 2·4 h per week of potential work productivity lost, respondents with moderate AD 9·6 h and respondents with severe AD 19·0 h.
Conclusions: Higher AD severity was associated with a greater negative impact on work productivity in adults. This impact is a burden not only for the patient but also for society and may provide incentives for treatment optimization and more effective management of AD. What's already known about this topic? Atopic dermatitis (AD) is associated with a high disease burden. AD has a negative impact on several aspects of health-related quality of life, one of which is work productivity. What does this study add? By using a population of participants with AD recruited from the National Health and Wellness Survey, which collects broad and representative data from the general population, survey data could be obtained from U.S. and European populations of patients with AD. The present study suggests an increasingly negative impact on work productivity with increasing severity of AD. The data indicate no regional differences in the impact of AD severity on work productivity.
© 2019 The Authors. British Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Figures
References
-
- Barbarot S, Auziere S, Gadkari A et al Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: results from an international survey. Allergy 2018; 73:1284–93. - PubMed
-
- Hanifin JM, Reed ML. A population‐based survey of eczema prevalence in the United States. Dermatitis 2007; 18:82–91. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI, Hanifin JM. Adult eczema prevalence and associations with asthma and other health and demographic factors: a US population‐based study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013; 132:1132–8. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI, Garg NK, Paller AS et al Sleep disturbances in adults with eczema are associated with impaired overall health: a US population‐based study. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135:56–66. - PubMed
-
- Harrop J, Chinn S, Verlato G et al Eczema, atopy and allergen exposure in adults: a population‐based study. Clin Exp Allergy 2007; 37:526–35. - PubMed

