Lithium-Aluminate-Catalyzed Hydrophosphination Applications
- PMID: 31260154
- PMCID: PMC6771573
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201906807
Lithium-Aluminate-Catalyzed Hydrophosphination Applications
Abstract
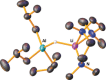
Synthesized, isolated, and characterized by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopic studies, lithium phosphidoaluminate iBu3 AlPPh2 Li(THF)3 has been tested as a catalyst for hydrophosphination of alkynes, alkenes, and carbodiimides. Based on the collective evidence of stoichiometric reactions, NMR monitoring studies, kinetic analysis, and DFT calculations, a mechanism involving deprotonation, alkyne insertion, and protonolysis is proposed for the [iBu3 AlHLi]2 aluminate catalyzed hydrophosphination of alkynes with diphenylphosphine. This study enhances further the development of transition-metal-free, atom-economical homogeneous catalysis using common sustainable main-group metals.
Keywords: aluminate; homogeneous catalysis; hydrophosphination; lithium; phosphines.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dillon K. B., Mathey F., Nixon J. F., Phosphorus: The carbon copy, Wiley, Chichester, 1998.
-
- None
-
- Glueck D. S., in C-X Bond Formation (Ed.: A. Vigalok), Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 65–100;
-
- Koshti V., Gaikwad S., Chikkali S. H., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 265, 52–73;
-
- Bange C. A., Waterman R., Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12598–12605. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

