Correlation of fatigue with other disease related and psychosocial factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: ACT-AXIS study
- PMID: 31261500
- PMCID: PMC6617279
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015947
Correlation of fatigue with other disease related and psychosocial factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: ACT-AXIS study
Abstract
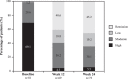
To assess the hypothesis if tocilizumab (TCZ) is effective on disease activity, and also its effect in fatigue and other clinical and psychological disease-related factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with TCZ.A 24-week, multicenter, prospective, observational study in patients with moderate to severe RA receiving TCZ after failure or intolerance to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or tumor necrosis factor-alpha was conducted.Of the 122 patients included, 85 were evaluable for effectiveness (85% female, 51.9 ± 12.5 years, disease duration 8.7 ± 7.4 years). Mean change in C-reactive protein level from baseline to week 12 was -11.2 ± 4.0 (P < .001). Mean Disease Activity Index score (DAS28) decreased from 5.5 ± 1.0 at baseline to 2.7 ± 1.3 (P < .001) at week 24. Mean change in Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy score was -5.4 ± 11.2 points at week 24. Multiple regression analysis showed that the improvement in DAS28, sleep, and depression explained 56% and 47% of fatigue variance at week 12 and 24, respectively.Tocilizumab is effective in reducing disease activity and results in a clinically significant improvement in fatigue, pain, swollen joint count, morning stiffness, sleepiness, depression, and DAS28; the last 3 were specifically identified as factors explaining fatigue variance with the use of TCZ in RA patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Hewlett S, Cockshott Z, Byron M, et al. Patients’ perceptions of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis: overwhelming, uncontrollable, ignored. Arthritis Rheum 2005;53:697–702. - PubMed
-
- Minnock P, Kirwan J, Bresnihan B. Fatigue is a reliable, sensitive and unique outcome measure in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:1533–6. - PubMed
-
- Minnock P, FitzGerald O, Bresnihan B. Women with established rheumatoid arthritis perceive pain as the predominant impairment of health status. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42:995–1000. - PubMed
-
- Pollard LC, Choy EH, Gonzalez J, et al. Fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis reflects pain, not disease activity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:885–9. - PubMed
-
- Repping-Wuts H, Fransen J, van AT, et al. Persistent severe fatigue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Nurs 2007;16:377–83. - PubMed

