Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis in patients affected by systemic sclerosis: What should the rheumatologist do?
- PMID: 31261523
- PMCID: PMC6617070
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016086
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis in patients affected by systemic sclerosis: What should the rheumatologist do?
Abstract
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE) is a rare new interstitial lung disease (ILD) characterized by the fibrotic thickening of the visceral pleura and subadjacent parenchymal areas of the upper lobes This study reveals that patients with ILD-SSc associated with chest HRCT evidence of PPFE require close and recurrent follow-up with periodic evaluation of lung function parameters, DLCO and chest HRCT. Rheumatologists should be aware of this new radiological finding which is accompanied by a negative prognosis, especially when associated with a progressive course. Patients with this radiological pattern need to be monitored with particular attention.
Conflict of interest statement
All these authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
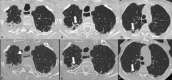
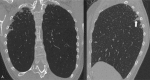
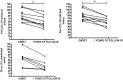
References
-
- Varga J, Trojanowska M, Kuwana M. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 2017;2:137–52.
-
- Rosenbaum JN, Butt YM, Johnson KA, et al. Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: a pattern of chronic lung injury. Hum Pathol 2015;46:137–46. - PubMed
-
- Reddy TL, Tominaga M, Hansell DM, et al. Pleuroparenchymalfibroelastosis: a spectrum of histopathological and imaging phenotypes. Eur Respir J 2012;40:377–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

