2-Ketogluconate Kinase from Cupriavidus necator H16: Purification, Characterization, and Exploration of Its Substrate Specificity
- PMID: 31261738
- PMCID: PMC6651773
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24132393
2-Ketogluconate Kinase from Cupriavidus necator H16: Purification, Characterization, and Exploration of Its Substrate Specificity
Abstract
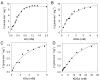
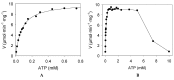
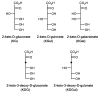
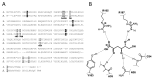
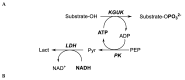
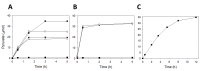
We have cloned, overexpressed, purified, and characterized a 2-ketogluconate kinase (2-dehydrogluconokinase, EC 2.7.1.13) from Cupriavidus necator (Ralstonia eutropha) H16. Exploration of its substrate specificity revealed that three ketoacids (2-keto-3-deoxy-d-gluconate, 2-keto-d-gulonate, and 2-keto-3-deoxy-d-gulonate) with structures close to the natural substrate (2-keto-d-gluconate) were successfully phosphorylated at an efficiency lower than or comparable to 2-ketogluconate, as depicted by the measured kinetic constant values. Eleven aldo and keto monosaccharides of different chain lengths and stereochemistries were also assayed but not found to be substrates. 2-ketogluconate-6-phosphate was synthesized at a preparative scale and was fully characterized for the first time.
Keywords: 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate; 2-ketogluconate; 2-ketogluconate kinase; 2-ketogulonate; Cupriavidus necator; biocatalysis; monosaccharides phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

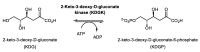

Similar articles
-
A propionate CoA-transferase of Ralstonia eutropha H16 with broad substrate specificity catalyzing the CoA thioester formation of various carboxylic acids.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Sep;97(17):7699-709. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4624-9. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23250223
-
Enzyme expression in Cupriavidus necator H16 for whole-cell biocatalysis.Methods Enzymol. 2025;714:195-218. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2025.01.079. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Methods Enzymol. 2025. PMID: 40288839
-
Homotaurine metabolized to 3-sulfopropanoate in Cupriavidus necator H16: enzymes and genes in a patchwork pathway.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):6052-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00678-09. Epub 2009 Jul 31. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19648235 Free PMC article.
-
[NiFe]-hydrogenases of Ralstonia eutropha H16: modular enzymes for oxygen-tolerant biological hydrogen oxidation.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;10(2-4):181-96. doi: 10.1159/000091564. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16645314 Review.
-
Design of inducible expression vectors for improved protein production in Ralstonia eutropha H16 derived host strains.J Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 10;235:92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.04.026. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27085887 Review.
Cited by
-
Two NADPH-dependent 2-ketogluconate reductases involved in 2-ketogluconate assimilation in Gluconobacter sp. strain CHM43.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Feb 19;91(2):e0250124. doi: 10.1128/aem.02501-24. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39878490 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Synthesis and Analysis of Biologically Active Phosphometabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3150. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043150. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vergne-Vaxelaire C., Mariage A., Petit J.-L., Fossey-Jouenne A., Guérard-Hélaine C., Darii E., Debard A., Nepert S., Pellouin V., Lemaire M., et al. Characterization of a thermotolerant ROK-type mannofructokinase from Streptococcus mitis: Application to the synthesis of phosphorylated sugars. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018;102:5569–5583. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9018-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fessner W.-D., Walter C. “Artificial metabolisms” for the asymmetric one-pot synthesis of branched-chain saccharides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1992;31:614–616. doi: 10.1002/anie.199206141. - DOI
-
- Zimmermann F.T., Schneider A., Schörken U., Sprenger G.A., Fessner W.-D. Efficient multi-enzymatic synthesis of d-xylulose 5-phosphate. Tetrahedron Asymmetry. 1999;10:1643–1646. doi: 10.1016/S0957-4166(99)00166-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

