In the human sperm nucleus, nucleosomes form spatially restricted domains consistent with programmed nucleosome positioning
- PMID: 31262721
- PMCID: PMC6679404
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.041368
In the human sperm nucleus, nucleosomes form spatially restricted domains consistent with programmed nucleosome positioning
Abstract
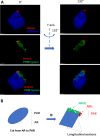
In human sperm, a fraction of its chromatin retains nucleosomes that are positioned on specific sequences containing genes and regulatory units essential for embryonic development. This nucleosome positioning (NP) feature provides an inherited epigenetic mark for sperm. However, it is not known whether there is a structural constraint for these nucleosomes and, if so, how they are localized in a three-dimensional (3D) context of the sperm nucleus. In this study, we examine the 3D organization of sperm chromatin and specifically determine its 3D localization of nucleosomes using structured illumination microscopy. A fraction of the sperm chromatin form nucleosome domains (NDs), visible as microscopic puncta ranging from 40 μm to 700 μm in diameter, and these NDs are precisely localized in the post acrosome region (PAR), outside the sperm's core chromatin. Further, NDs exist mainly in sperm from fertile men in a pilot survey with a small sample size. Together, this study uncovers a new spatially-restricted sub-nuclear structure containing NDs that are consistent with NPs of the sperm, which might represent a novel mark for healthy sperm in human.
Keywords: Chromatin; Domain; Human sperm; Nucleosome.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Adenot P. G., Mercier Y., Renard J. P. and Thompson E. M. (1997). Differential H4 acetylation of paternal and maternal chromatin precedes DNA replication and differential transcriptional activity in pronuclei of 1-cell mouse embryos. Development 124, 4615-4625. - PubMed
-
- Bloch D. P. and Teng C. (1969). The synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid and nuclear histone of the X chromosome of the Rehnia spinosus spermatocyte. J. Cell Sci. 5, 321-332. - PubMed
-
- Botezatu A., Socolov R., Socolov D., Iancu I. V. and Anton G. (2014). Methylation pattern of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N promoters in oligoasthenospermia: a case-control study. Reprod. Biomed. Online 28, 225-231. 10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.10.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

