Monocyte and macrophage subtypes as paired cell biomarkers for coronary artery disease
- PMID: 31264265
- PMCID: PMC6717038
- DOI: 10.1113/EP087827
Monocyte and macrophage subtypes as paired cell biomarkers for coronary artery disease
Abstract
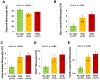
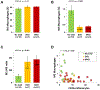
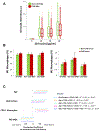
New findings: What is the central question of this study? Are circulating monocyte markers correlated with their derived macrophage polarization patterns and coronary artery disease severity? What is the main finding and its importance? There was an inverse relationship between circulating CD16+ monocytes (high) and M2 macrophages (low) that marked coronary disease severity, and the differences in polarization of macrophages were seen despite a week of cell culture ex vivo. This study highlights the importance, and potential prognostic implications, of circulating monocyte and descendant macrophage phenotypes in coronary artery disease.
Abstract: Monocytes and macrophages are central to atherosclerosis, but how they combine to mark progression of human coronary artery disease (CAD) is unclear. We tested whether patients' monocyte subtypes paired with their derived macrophage profiles were correlated with extent of CAD. Peripheral blood was collected from 40 patients undergoing cardiac catheterization, and patients were categorized as having no significant CAD, single vessel disease or multivessel disease according to the number of affected coronary arteries. Mononuclear cells were measured for the monocyte markers CD14 and CD16 by flow cytometry, and separate monocytes were cultured into macrophages over 7 days and measured for the polarization markers CD86 and CD206. At baseline, patients with a greater CAD burden were older, with higher rates of statin, β-blocker and antiplatelet drug use, whereas other characteristics were similar across the spectrum of coronary disease. CD16+ (both intermediate and non-classical) monocytes were elevated in patients with single vessel and multivessel disease compared with those without significant CAD (P < 0.05), whereas regulatory M2 macrophages (CD206+ ) were decreased in patients with single vessel and multivessel disease (P < 0.001). An inverse relationship between paired CD16+ monocytes and M2 macrophages marked CAD severity. On multivariable linear regression, CAD severity was associated, along with age and traditional cardiovascular risk factors, with CD16+ monocytes (directly) and M2 macrophages (inversely). Circulating monocytes may influence downstream polarization of lesional macrophages, and these measures of monocyte and macrophage subtypes hold potential as biomarkers in CAD.
Keywords: cell-based biomarkers; coronary artery disease; macrophage; monocyte.
© 2019 The Authors. Experimental Physiology © 2019 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bekkering S, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM, Netea MG & Riksen NP (2015). The epigenetic memory of monocytes and macrophages as a novel drug target in atherosclerosis. Clin Ther 37, 914–923. - PubMed
-
- Bisgaard LS, Mogensen CK, Rosendahl A, Cucak H, Nielsen LB, Rasmussen SE & Pedersen TX (2016). Bone marrow-derived and peritoneal macrophages have different inflammatory response to oxLDL and M1/M2 marker expression – implications for atherosclerosis research. Sci Rep; DOI: 10.1038/srep35234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cappellari R, D’Anna M, Bonora BM, Rigato M, Cignarella A, Avogaro A & Fadini GP (2017). Shift of monocyte subsets along their continuum predicts cardiovascular outcomes. Atherosclerosis 266, 95–102. - PubMed
-
- Chellan B, Reardon CA, Getz GS & Hofmann Bowman MA (2016). Enzymatically Modified Low-Density Lipoprotein Promotes Foam Cell Formation in Smooth Muscle Cells via Macropinocytosis and Enhances Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36, 1101–1113. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

