MWCNT-7 administered to the lung by intratracheal instillation induces development of pleural mesothelioma in F344 rats
- PMID: 31265162
- PMCID: PMC6676138
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14121
MWCNT-7 administered to the lung by intratracheal instillation induces development of pleural mesothelioma in F344 rats
Abstract
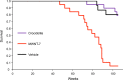
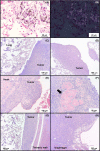
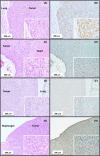
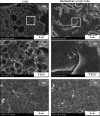
Multi-walled carbon nanotube-7 (MWCNT-7) fibers are biopersistent and have a structure similar to asbestos. MWCNT-7 has been shown to induce malignant mesothelioma when administered by intrascrotal or intraperitoneal injection in rats and mice, and an inhalation study demonstrated that rats exposed to respirable MWCNT-7 developed lung tumors. MWCNT-N, which is similar to MWCNT-7, was shown to induce both lung tumors and malignant mesothelioma in rats when administered by trans-tracheal intrapulmonary spraying (TIPS). The present study was performed to investigate the carcinogenicity of MWCNT-7 when administered by the TIPS method. Ten-week-old male F344/Crj rats were divided into 3 groups and administered 0.5 mL vehicle, 0.250 μg/mL MWCNT-7 or 0.250 μg/mL crocidolite once a week for 12 weeks (total doses of 1.5 mg/rat) and then observed for up to 104 weeks. Rats in the MWCNT-7 group began to die from pathologies associated with the development of malignant mesothelioma 35 weeks after the final TIPS administration. Overall, the incidence of malignant mesothelioma in the MWCNT-7 group was significantly higher than in the vehicle or crocidolite groups.
Keywords: MWCNT-7; inhalation toxicity; intra-tracheal intra-pulmonary spraying; malignant mesothelioma; rat.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative carcinogenicity study of a thick, straight-type and a thin, tangled-type multi-walled carbon nanotube administered by intra-tracheal instillation in the rat.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020 Oct 15;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00382-y. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 33054855 Free PMC article.
-
Multiwalled carbon nanotubes intratracheally instilled into the rat lung induce development of pleural malignant mesothelioma and lung tumors.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):924-35. doi: 10.1111/cas.12954. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27098557 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinogenic effect of potassium octatitanate (POT) fibers in the lung and pleura of male Fischer 344 rats after intrapulmonary administration.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019 Sep 2;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12989-019-0316-2. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31477126 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant Mesothelioma and Its Non-Asbestos Causes.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018 Jun;142(6):753-760. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0365-RA. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29480760 Review.
-
Mesothelioma and analysis of tissue fiber content.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;189:79-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-10862-4_6. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21479897 Review.
Cited by
-
Frequent homozygous deletion of Cdkn2a/2b in tremolite-induced malignant mesothelioma in rats.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1180-1192. doi: 10.1111/cas.14358. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32080953 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrotic pulmonary dust foci is an advanced pneumoconiosis lesion in rats induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in a 2-year inhalation study.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2025 Apr 18;22(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12989-025-00623-y. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40247355 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the toxicity and carcinogenicity of double-walled carbon nanotubes in the rat lung after intratracheal instillation: a two-year study.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022 Apr 22;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12989-022-00469-8. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35449069 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Single and Multiple Intratracheal Administrations for Pulmonary Toxic Responses of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Rats.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Dec 16;14(24):2019. doi: 10.3390/nano14242019. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728555 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative carcinogenicity study of a thick, straight-type and a thin, tangled-type multi-walled carbon nanotube administered by intra-tracheal instillation in the rat.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020 Oct 15;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00382-y. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 33054855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donaldson K, Murphy F, Schinwald A, Duffin R, Poland CA. Identifying the pulmonary hazard of high aspect ratio nanoparticles to enable their safety‐by‐design. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011;6:143‐156. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto Y, Nakae D, Fukumori N, et al. Induction of mesothelioma by a single intrascrotal administration of multi‐wall carbon nanotube in intact male Fischer 344 rats. J Toxicol Sci. 2009;34:65‐76. - PubMed
-
- Takagi A, Hirose A, Nishimura T, et al. Induction of mesothelioma in p53 + /− mouse by intraperitoneal application of multi‐wall carbon nanotube. J Toxicol Sci. 2008;33:105‐116. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5th Term Long-Range Research Initiative (2017) by Japan Chemical Industry Association
- H22-kagaku-ippan-005/Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- H22-kagaku-shitei-004/Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- H25-kagaku-ippan-004/Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- H27-kagaku-shitei-004/Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

