MUNC13-1 heterozygosity does not alter voluntary ethanol consumption or sensitivity in mice
- PMID: 31265903
- PMCID: PMC7043798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.06.007
MUNC13-1 heterozygosity does not alter voluntary ethanol consumption or sensitivity in mice
Abstract
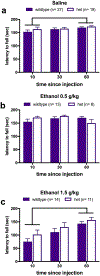
The role of the munc13-1 presynaptic protein in alcohol-related behaviors has been little-studied, despite being a known site of action for ethanol binding. Munc13-1 is an active zone protein that plays a vital role in vesicle maturation and the release of neurotransmitters in excitatory neurons. Ethanol binds munc13-1, which decreases its functionality. In Drosophila, loss of the homologous protein Dunc13 is associated with an increase in ethanol preference, and is associated with a resistance to sedation following ethanol exposure. The current study assessed the effects of munc13-1 heterozygosity on ethanol sensitivity and consumption in mice, as well as on learning and anxiety-like behaviors, which can influence alcohol intake. Wild-type and mutant mice underwent 6 cycles of drinking-in-the-dark (DID) as well as rotarod testing following ethanol injection, to probe for differences in ethanol consumption and sensitivity, respectively. We did not detect genotype-based differences in our measures of anxiety, spatial learning, ethanol consumption, or ethanol sensitivity. However, heterozygotes showed increased use of a spatial navigation strategy in a dual-solution water maze, as opposed to a stimulus-response strategy. To summarize, although reduction of Dunc13 in flies produces clear effects on ethanol consumption and sensitivity, heterozygosity for munc13-1 does not, potentially due to compensatory adaptation by other munc-13 isoforms.
Keywords: Addiction; Anxiety; Cognition; Spatial learning; Tolerance.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, & Young ER (1993). Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 112(4), 503–510. - PubMed
-
- Betz A, Okamoto M, Benseler F, & Brose N (1997). Direct interaction of the rat unc-13 homologue Munc13-1 with the N terminus of syntaxin. J Biol Chem, 272(4), 2520–2526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

