Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for the Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins and Their Glucosides in Wheat
- PMID: 31266143
- PMCID: PMC6669535
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11070380
Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for the Determination of T-2 and HT-2 Toxins and Their Glucosides in Wheat
Abstract
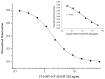
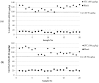
T-2 and HT-2 toxins and their main modified forms (T-2 glucoside and HT-2 glucoside) may co-occur in cereals and cereal-based products. A fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA) was developed for the simultaneous determination of T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin and relevant glucosides, expressed as sum. The developed FPIA, using a HT-2-specific antibody, showed high sensitivity (IC50 = 2.0 ng/mL) and high cross-reactivity (100% for T-2 toxin and 80% for T-2 and HT-2 glucosides). The FPIA has been used to develop two rapid and easy-to-use methods using two different extraction protocols, based on the use of organic (methanol/water, 90:10, v/v) and non-organic (water) solvents, for the determination of these toxins in wheat. The two proposed methods showed analytical performances in terms of sensitivity (LOD 10 µg/kg) recovery (92-97%) and precision (relative standard deviations ≤13%), fulfilling the criteria for acceptability of an analytical method for the quantitative determination of T-2 and HT-2 toxins established by the European Union. Furthermore, the methods were then validated in accordance with the harmonized guidelines for the validation of screening methods included in the Regulation (EU) No. 519/2014. The satisfactory analytical performances, in terms of intermediate precision (≤25%), cut-off level (80 and 96 µg/kg for the two methods) and rate of false positives (<0.1%) confirmed the applicability of the proposed methods as screening method for assessing the content of these toxins in wheat at the EU indicative levels reported for T-2 and HT-2 toxins.
Keywords: HT-2 glucoside; HT-2 toxin; T-2 glucoside; T-2 toxin; fluorescence polarization immunoassay; screening method; validation study; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Canady R.A., Coker R.D., Egan S.K., Krska R., Olsen M., Resnik S., Schlatter J. T-2 and HT-2 toxins. In: WHO/FAO, editor. Safety Evaluation of Certain Mycotoxins in Food. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2001. [(accessed on 24 April 2019)]. pp. 557–638. (WHO Food Additives Series 47, FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 74). Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-bc528e.pdf.
-
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of T-2 and HT-2 toxin in food and feed. EFSA J. 2011;9:2481. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2481. - DOI
-
- Pettersson H. Toxicity and risks with T-2 and HT-2 toxins in cereals. Plant Breed. Seed Sci. 2011;64:65–74. doi: 10.2478/v10129-011-0029-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

