Comparative proteomic analysis reveals drug resistance of Staphylococcus xylosus ATCC700404 under tylosin stress
- PMID: 31266490
- PMCID: PMC6604186
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-019-1959-9
Comparative proteomic analysis reveals drug resistance of Staphylococcus xylosus ATCC700404 under tylosin stress
Abstract
Background: As a kind of opportunist pathogen, Staphylococcus xylosus (S. xylosus) can cause mastitis. Antibiotics are widely used for treating infected animals and tylosin is a member of such group. Thus, the continuous use of antibiotics in dairy livestock enterprise will go a long way in increasing tylosin resistance. However, the mechanism of tylosin-resistant S. xylosus is not clear. Here, isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ)-based quantitative proteomics methods was used to find resistance-related proteins.
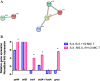
Results: We compared the differential expression of S. xylosus in response to tylosin stress by iTRAQ. A total of 155 proteins (59 up-regulated, 96 down-regulated) with the fold-change of >1.2 or <0.8 (p value ≤0.05) were observed between the S. xylosus treated with 1/2 MIC (0.25 μg/mL) tylosin and the untreated S. xylosus. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that these proteins play important roles in stress-response and transcription. Then, in order to verify the relationship between the above changed proteins and mechanism of tylosin-resistant S. xylosus, we induced the tylosin-resistant S. xylosus, and performed quantitative PCR analysis to verify the changes in the transcription proteins and the stress-response proteins in tylosin-resistant S. xylosus at the mRNA level. The data displayed that ribosomal protein L23 (rplw), thioredoxin(trxA) and Aldehyde dehydrogenase A(aldA-1) are up-regulated in the tylosin-resistant S. xylosus, compared with the tylosin-sensitive strains.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate the important of stress-response and transcription in the tylosin resistance of S. xylosus and provide an insight into the prevention of this resistance, which would aid in finding new medicines .
Keywords: Aldehyde dehydrogenase a;; Drug-resistance; Ribosomal protein L23; Staphylococcus xylosus; Thioredoxin; Tylosin; iTRAQ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tremblay YDN, Lamarche D, Chever P, et al. Characterization of the ability of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from the milk of Canadian farms to form biofilms. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96(1):234. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KL, Azizoglu RO. Detection and causes of bovine mastitis with emphasis on Staphylococcus aureus. Encyclopedia of Agriculture & Food Systems. 2014. pp. 435–440.
-
- Frey Y, Rodriguez JP, Thomann A, et al. Genetic characterization of antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis milk. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96(4):2247–2257. - PubMed
-
- Entorf M, Feßler AT, Kadlec K, et al. Tylosin susceptibility of staphylococci from bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol. 2014;171(3–4):368–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

