Molecular tuning of farnesoid X receptor partial agonism
- PMID: 31266946
- PMCID: PMC6606567
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10853-2
Molecular tuning of farnesoid X receptor partial agonism
Abstract
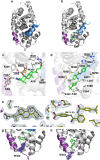
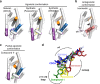
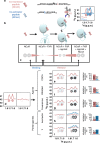
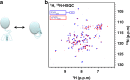
The bile acid-sensing transcription factor farnesoid X receptor (FXR) regulates multiple metabolic processes. Modulation of FXR is desired to overcome several metabolic pathologies but pharmacological administration of full FXR agonists has been plagued by mechanism-based side effects. We have developed a modulator that partially activates FXR in vitro and in mice. Here we report the elucidation of the molecular mechanism that drives partial FXR activation by crystallography- and NMR-based structural biology. Natural and synthetic FXR agonists stabilize formation of an extended helix α11 and the α11-α12 loop upon binding. This strengthens a network of hydrogen bonds, repositions helix α12 and enables co-activator recruitment. Partial agonism in contrast is conferred by a kink in helix α11 that destabilizes the α11-α12 loop, a critical determinant for helix α12 orientation. Thereby, the synthetic partial agonist induces conformational states, capable of recruiting both co-repressors and co-activators leading to an equilibrium of co-activator and co-repressor binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Binding mechanism of the farnesoid X receptor marine antagonist suvanine reveals a strategy to forestall drug modulation on nuclear receptors. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel ligands.J Med Chem. 2013 Jun 13;56(11):4701-17. doi: 10.1021/jm400419e. Epub 2013 May 24. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23656455
-
Design and identification of a new farnesoid X receptor (FXR) partial agonist by computational structure-activity relationship analysis: Ligand-induced H8 helix fluctuation in the ligand-binding domain of FXR may lead to partial agonism.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Jun 1;41:128026. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128026. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33839252
-
Farnesoid X receptor agonists suppress hepatic apolipoprotein CIII expression.Gastroenterology. 2003 Aug;125(2):544-55. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00896-5. Gastroenterology. 2003. PMID: 12891557
-
Farnesoid-X Receptor (FXR) as a Promising Pharmaceutical Target in Atherosclerosis.Curr Med Chem. 2017 May 31;24(11):1147-1157. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170124151940. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28120707 Review.
-
Marine sponge steroids as nuclear receptor ligands.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Nov;33(11):591-601. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23000093 Review.
Cited by
-
Simulations Reveal Unique Roles for the FXR Hinge in the FXR-RXR Nuclear Receptor Heterodimer.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024 Nov 27;5(1):194-203. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.4c00105. eCollection 2025 Feb 19. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024. PMID: 39990948 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids mediated potential functional interaction between FXR and FATP5 in the regulation of Lipid Metabolism.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 14;16(13):2308-2322. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44774. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32760200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery, optimization, and evaluation of non-bile acid FXR/TGR5 dual agonists.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88493-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911126 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Farnesoid X Receptor in Tumor and the Tumor Microenvironment: Implication for Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 19;25(1):6. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010006. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Selectivity of FXR, LXRs, CAR, and RORγ Pharmaceutical Ligands With Reporter Cell Lines.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 24;11:1122. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01122. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32792956 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

