Nasal delivery of donepezil HCl-loaded hydrogels for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 31266990
- PMCID: PMC6606601
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46032-y
Nasal delivery of donepezil HCl-loaded hydrogels for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
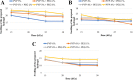
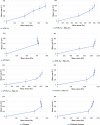
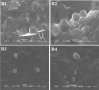
This study aims to prepare, characterize and evaluate the pharmacokinetics of liposomal donepezil HCl (LDH) dispersed into thiolated chitosan hydrogel (TCH) in rabbits. Various hydrogels including TCH were prepared, and after characterization, TCH was selected for subsequent evaluations, due to the promising results. TCH was then incorporated with LDH prepared by reverse phase evaporation method. The hydrogel was characterized using scanning electron microscope, dialysis membrane technique, and ultra-performance liquid chromatography methods. The optimized resultant was then evaluated in terms of pharmacokinetics in an in vivo environment. The mean size of LDH and drug entrapment efficiency were 438.7 ± 28.3 nm and 62.5% ± 0.6, respectively. The controlled drug release pattern results showed that the half-life of the loaded drug was approximately 3.5 h. Liposomal hydrogel and free liposomes were more stable at 4 °C compared to those in 20 °C. The pharmacokinetics study in the rabbit showed that the optimized hydrogel increased the mean peak drug concentration and area under the curve by 46% and 39%, respectively, through nasal route compared to the oral tablets of DH. Moreover, intranasal delivery of DH through liposomal hydrogel increased the mean brain content of the drug by 107% compared to the oral DH tablets. The results suggested that liposomes dispersed into TCH is a promising device for the nasal delivery of DH and can be considered for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Di Domenico F, Barone E, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA. The triangle of death in Alzheimer’s disease brain: the aberrant cross-talk among energy metabolism, mammalian target of rapamycin signaling, and protein homeostasis revealed by redox proteomics. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 2017;26:364–387. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6759. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Espinoza LC, et al. Development of a Nasal Donepezil-loaded Microemulsion for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: in vitro and ex vivo Characterization. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 2018;17:43–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

