High frequency electrical stimulation promotes expression of extracellular matrix proteins from human astrocytes
- PMID: 31267326
- PMCID: PMC9277158
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-019-04890-9
High frequency electrical stimulation promotes expression of extracellular matrix proteins from human astrocytes
Abstract
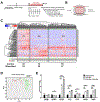
Therapeutic benefits of deep brain stimulation (DBS), a neurosurgical treatment for certain movement disorders and other neurologic conditions, are well documented, but DBS mechanisms remain largely unexplained. DBS is thought to modulate pathological neural activity. However, although astrocytes, the most numerous cell type in the brain, play a significant role in neurotransmission, chemical homeostasis and synaptic plasticity, their role in DBS has not been fully examined. To investigate astrocytic function in DBS, we applied DBS-like high frequency electrical stimulation for 24 h to human astrocytes in vitro and analyzed single cell transcriptome mRNA profile. We found that DBS-like high frequency stimulation negatively impacts astrocyte metabolism and promotes the release of extracellular matrix (matricellular) proteins, including IGFBP3, GREM1, IGFBP5, THBS1, and PAPPA. Our results suggest that astrocytes are involved in the long-term modulation of extra cellular matrix environments and that they may influence persistent cell-to-cell interaction and help maintain neuromodulation over time.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Deep brain stimulation; Extracellular matrix; Matricellular protein; Single cell transcriptome.
Figures

References
-
- Basso M, Berlin J, Xia L, Sleiman SF, Ko B, Haskew-Layton R, Kim E, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA, Iismaa SE, Willis D, Cho S, Ratan RR (2012) Transglutaminase inhibition protects against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death downstream of pathological ERK activation. J Neurosci 32:6561–6569. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekar L, Libionka W, Tian GF, Xu Q, Torres A, Wang X, Lovatt D, Williams E, Takano T, Schnermann J, Bakos R, Nedergaard M (2008) Adenosine is crucial for deep brain stimulation-mediated attenuation of tremor. Nat Med 14:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL, Pollak P, Louveau A, Henry S, de Rougemont J (1987) Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson disease. Appl Neurophysiol 50:344–346. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

