Identification and diagnostic value of pleural fluid periostin and serum periostin of malignant pleural effusions in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31268191
- PMCID: PMC6757121
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22943
Identification and diagnostic value of pleural fluid periostin and serum periostin of malignant pleural effusions in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available for the diagnostic value, and the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of pleural fluid periostin (pPOSTN) and serum periostin (sPOSTN) in malignant pleural effusion (MPE) caused by non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: We collected 84 pleural effusion samples, including 44 cases of MPE caused by NSCLC and 40 cases of benign pleural effusions (BPEs) from August 2018 to January 2019. The pPOSTN, sPOSTN, pleural fluid lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH), pleural effusion adenosine deaminase (pADA), pleural effusion total protein (pTP), pleural fluid glucose (pGLU), pleural effusion leukocyte count (pWBC), pleural effusion red cell count (pRBC), pleural effusion carbohydrate antigen 199 (pCA199), pleural fluid carbohydrate antigen 125 (pCA125), pleural effusion ferritin (pFer), serum total protein (sTP), and serum C-reactive protein (sCRP) were tested, and the obtained data were analyzed by statistical software.
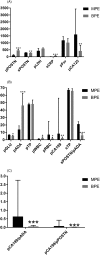
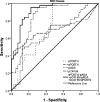
Results: Compared to the BPE group, the pPOSTN level in the MPE group was observably lower, while the levels of sPOSTN, sPOSTN/pADA, pCA199/pADA, and pCA199/pPOSTN increased. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed that the area under the ROC curve (AUC) (=0.844, 0.847, 0.841) of sPOSTN/pADA, pCA199/pADA, and pCA199/pPOSTN (cutoff = 11.86, 0.244, 0.015) was observably higher than other indicators for the diagnosis of MPE caused by NSCLC. Thus, the combined detection of pPOSTN, pCA125/pPOSTN, and pCA125/sCRP suggested that the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity was 0.912%, 95.45%, and 77.50% at the cutoff 0.317 and diagnostic performance was higher than sPOSTN/pADA or pCA199/pADA or pCA199/pPOSTN.
Conclusion: Combined detection of sPOSTN/pADA, pCA199/pADA, and pCA199/pPOSTN can be used as a good indicator for MPE caused by NSCLC.
Keywords: malignant pleural effusion; non-small-cell lung cancer; periostin.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(3):177‐193. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69‐90. - PubMed
-
- Morgensztern D, Waqar S, Subramanian J, Trinkaus K, Govindan R. Prognostic impact of malignant pleural effusion at presentation in patients with metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(10):1485‐1489. - PubMed
-
- Braunschweig R, Yan P, Guilleret I, et al. Detection of malignant effusions: comparison of a telomerase assay and cytologic examination. Diagn Cytopathol. 2001;24(3):174‐180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

