Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling for the Prediction of CYP2D6-Mediated Gene-Drug-Drug Interactions
- PMID: 31268632
- PMCID: PMC6709421
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12411
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling for the Prediction of CYP2D6-Mediated Gene-Drug-Drug Interactions
Abstract
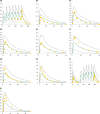
The aim of this work was to predict the extent of Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6)-mediated drug-drug interactions (DDIs) in different CYP2D6 genotypes using physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling. Following the development of a new duloxetine model and optimization of a paroxetine model, the effect of genetic polymorphisms on CYP2D6-mediated intrinsic clearances of dextromethorphan, duloxetine, and paroxetine was estimated from rich pharmacokinetic profiles in activity score (AS)1 and AS2 subjects. We obtained good predictions for the dextromethorphan-duloxetine interaction (Ratio of predicted over observed area under the curve (AUC) ratio (Rpred/obs ) 1.38-1.43). Similarly, the effect of genotype was well predicted, with an increase of area under the curve ratio of 28% in AS2 subjects when compared with AS1 (observed, 33%). Despite an approximately twofold underprediction of the dextromethorphan-paroxetine interaction, an Rpred/obs of 0.71 was obtained for the effect of genotype on the area under the curve ratio. Therefore, PBPK modeling can be successfully used to predict gene-drug-drug interactions (GDDIs). Based on these promising results, a workflow is suggested for the generic evaluation of GDDIs and DDIs that can be applied in other situations.
© 2019 The Authors CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Marengoni, A. et al Understanding adverse drug reactions in older adults through drug‐drug interactions. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 25, 843–846 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Zheng, W.Y. et al Drug‐drug interactions and their harmful effects in hospitalised patients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 74, 15–27 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Storelli, F. , Samer, C. , Reny, J.L. , Desmeules, J. & Daali, Y. Complex drug‐drug‐gene‐disease interactions involving cytochromes P450: systematic review of published case reports and clinical perspectives. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 57, 1267–1293 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Lin, J.H. & Lu, A.Y. Interindividual variability in inhibition and induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41, 535–567 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

