A Psycholinguistic Framework for Diagnosis and Treatment Planning of Developmental Speech Disorders
- PMID: 31269495
- PMCID: PMC7050667
- DOI: 10.1159/000499426
A Psycholinguistic Framework for Diagnosis and Treatment Planning of Developmental Speech Disorders
Abstract
Background: Differential diagnosis and treatment planning of developmental speech disorders (DSD) remains a major challenge in paediatric speech-language pathology. Different classification systems exist, in which subtypes are differentiated based on their theoretical cause and in which the definitions generally refer to speech production processes. Accordingly, various intervention methods have been developed aiming at different parts of the speech production process. Diagnostic classification in these systems, however, is primarily based on a description of behavioural speech symptoms rather than on underlying deficits.
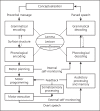
Purpose: In this paper, we present a process-oriented approach to diagnosis and treatment planning of DSD. Our framework comprises two general diagnostic categories: developmental delay and developmental disorder. Within these categories, treatment goals/targets and treatment methods are formulated at the level of processes and rules/representations.
Conclusion: A process-oriented approach to diagnosis and treatment planning holds important advantages, offering direct leads for treatment aimed at the underlying impairment, tailored to the specific needs of the individual and adjusted to the developmental trajectory.
Keywords: Differential diagnosis; Speech development; Speech disorders; Treatment planning.
© 2019 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Psycholinguistic assessment of developmental speech disorders.Eur J Disord Commun. 1993;28(4):331-48. doi: 10.3109/13682829309041469. Eur J Disord Commun. 1993. PMID: 8312650
-
How should children with speech sound disorders be classified? A review and critical evaluation of current classification systems.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2013 Jan;48(1):25-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-6984.2012.00195.x. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2013. PMID: 23317382
-
The contribution of polysyllabic words in clinical decision making about children's speech.Clin Linguist Phon. 2008 Apr-May;22(4-5):345-53. doi: 10.1080/02699200801919240. Clin Linguist Phon. 2008. PMID: 18415734 Review.
-
Issues contrasting adult acquired versus developmental apraxia of speech.Semin Speech Lang. 2002 Nov;23(4):257-66. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-35804. Semin Speech Lang. 2002. PMID: 12461725 Review.
-
Phonological and morphophonological effects on grammatical development in children with specific language impairment.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2015 Jul;50(4):516-28. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12152. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2015. PMID: 25703395 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Concurrent Validity Between Two Sound Sequencing Tasks Used to Identify Childhood Apraxia of Speech in School-Age Children.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2021 Jun 18;30(3S):1580-1588. doi: 10.1044/2020_AJSLP-20-00108. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33684299 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome measures for children with speech sound disorder: an umbrella review.BMJ Open. 2024 Apr 29;14(4):e081446. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081446. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38684261 Free PMC article.
-
How to cut the pie is no piece of cake: Toward a process-oriented approach to assessment and diagnosis of speech sound disorders.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024 Nov-Dec;59(6):2158-2180. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12934. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 37483105 Review.
-
Apraxia of speech and the study of speech production impairments: Can we avoid further confusion? Reply to Romani (2021).Cogn Neuropsychol. 2021 May-Jun;38(4):309-317. doi: 10.1080/02643294.2021.2009790. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2021. PMID: 34881683 Free PMC article.
-
To Lump or to Split? Possible Subtypes of Apraxia of Speech.Aphasiology. 2020;35(4):592-613. doi: 10.1080/02687038.2020.1836319. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Aphasiology. 2020. PMID: 33981126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell TF, Functional treatment outcomes in young children with motor speech disorders . Clinical Management of Motor Speech Disorders in Children. In: Caruso A, Strand E, editors. New York: Thieme; 1999. pp. pp. 385–96.
-
- Conti-Ramsden G, Botting N. Social difficulties and victimization in children with SLI at 11 years of age. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2004 Feb;47((1)):145–61. - PubMed
-
- van Daal J, Verhoeven L, van Balkom H. Behaviour problems in children with language impairment. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007 Nov;48((11)):1139–47. - PubMed
-
- McCormack J, McLeod S, McAllister L, Harrison LJ. A systematic review of the association between childhood speech impairment and participation across the lifespan. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2009;11((2)):155–70.
-
- Felsenfeld S, Broen PA, McGue M. A 28-year follow-up of adults with a history of moderate phonological disorder: educational and occupational results. J Speech Hear Res. 1994 Dec;37((6)):1341–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources