Toward a Harmonized and Standardized Protocol for the Determination of Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil (VOO). The Pros of a Fit for the Purpose Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) Procedure
- PMID: 31269664
- PMCID: PMC6651398
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24132429
Toward a Harmonized and Standardized Protocol for the Determination of Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil (VOO). The Pros of a Fit for the Purpose Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) Procedure
Abstract
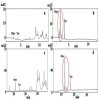
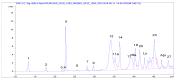
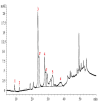
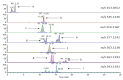
Τoward a harmonized and standardized procedure for the determination of total hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol content in virgin olive oil (VOO), the pros of a recently published in house validated ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) protocol are discussed comparatively with those of other procedures that determine directly or indirectly the compounds hosted under the health claim on "olive oil polyphenols" (EC regulation 432/2012). Authentic VOOs were analyzed with five different liquid chromatographic separation protocols and 1H-NMR one in five different laboratories with expertise in VOO phenol analysis within three months. Data comparison indicated differences in absolute values. Method comparison using appropriate tools (Passing-Bablok regression and Bland Altman analyses) for all protocols vs. the UHPLC one indicated slight or statistically significant differences. The results were also discussed in terms of cost effectiveness, detection means, standard requirements and ways to calculate the total hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol content. Findings point out that the in-house validated fit for the purpose UHPLC protocol presents certain pros that should be exploited by the interested parties. These are the simplicity of sample preparation, fast elution time that increase the number of samples analyzed per day and integration of well-resolved peaks with the aid of only two commercially available external standards. Importance of correction factors in the calculations is stressed.
Keywords: 1H-NMR spectroscopy; European Commission Regulation 432/2012; HPLC-DAD; LC-HRMS; UHPLC-DAD; health claim; hydroxytyrosol; standardization; tyrosol; virgin olive oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In House Validated UHPLC Protocol for the Determination of the Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil Fit for the Purpose of the Health Claim Introduced by the EC Regulation 432/2012 for "Olive Oil Polyphenols".Molecules. 2019 Mar 16;24(6):1044. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061044. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30884804 Free PMC article.
-
The EFSA Health Claim on Olive Oil Polyphenols: Acid Hydrolysis Validation and Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Determination in Italian Virgin Olive Oils.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2179. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112179. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185655 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing analytical requirements to support health claims on "olive oil polyphenols" (EC Regulation 432/2012).J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Mar 26;62(12):2459-61. doi: 10.1021/jf5005918. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24576103
-
NMR spectroscopy: a powerful tool for the analysis of polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Mar 30;100(5):1842-1851. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10173. Epub 2019 Dec 28. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31802495 Review.
-
Hydroxytyrosol in the Prevention of the Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 20;9(3):306. doi: 10.3390/nu9030306. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28335507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Virgin Olive Oil from cv. Chondrolia Chalkidikis and Chalkidiki (Greece) to Bear Health Claims according to the European Legislation.Molecules. 2021 May 26;26(11):3184. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113184. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34073383 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Vibrational Spectroscopic Techniques for the Detection of Bio-Active Compounds in Virgin Olive Oils: A Comprehensive Review.Foods. 2024 Dec 3;13(23):3894. doi: 10.3390/foods13233894. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39682966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-cancer Effect of Olea europaea L. Products: a Review.Curr Nutr Rep. 2021 Mar;10(1):99-124. doi: 10.1007/s13668-021-00350-8. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Curr Nutr Rep. 2021. PMID: 33683579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concentration of Potentially Bioactive Compounds in Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oils from Various Sources by Using LC-MS and Multivariate Data Analysis.Foods. 2020 Aug 13;9(8):1120. doi: 10.3390/foods9081120. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32823794 Free PMC article.
-
Oleocanthal Quantification Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Polyphenols HPLC Analysis of Olive Oil from the Bianchera/Belica Cultivar.Molecules. 2021 Jan 5;26(1):242. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010242. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33466567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsimidou M. Polyphenols and quality of virgin olive oil in retrospect. Ital. J. Food Sci. 1998;10:99–116.
-
- Tsimidou M.Z. Analytical methodologies: Phenolic compounds related to olive oil taste issues. In: Aparicio-Ruiz R., Harwood J., editors. Handbook of Olive Oil. 2nd ed. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 2013. pp. 311–333.
-
- Hrncirik K., Fritsche S. Comparability and reliability of different techniques for the determination of phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004;106:540–549. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200400942. - DOI
-
- Tsimidou M. Analysis of virgin olive oil polyphenols. Semin. Food Anal. 1999;4:13–29.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

