Effects of Cholesterol on Water Permittivity of Biomimetic Ion Pair Amphiphile Bilayers: Interplay between Membrane Bending and Molecular Packing
- PMID: 31269714
- PMCID: PMC6651711
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20133252
Effects of Cholesterol on Water Permittivity of Biomimetic Ion Pair Amphiphile Bilayers: Interplay between Membrane Bending and Molecular Packing
Abstract
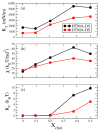
Ion pair amphiphile (IPA), a molecular complex composed of a pair of cationic and anionic amphiphiles, is an inexpensive phospholipid substitute to fabricate vesicles with various pharmaceutical applications. Modulating the physicochemical and permeation properties of IPA vesicles are important for carrier designs. Here, we applied molecular dynamics simulations to examine the cholesterol effects on the structures, mechanics, and water permittivity of hexadecyltrimethylammonium-dodecylsulfate (HTMA-DS) and dodecyltrimethylammonium- hexadecylsulfate (DTMA-HS) IPA bilayers. Structural and mechanical analyses indicate that both IPA systems are in gel phase at 298 K. Adding cholesterol induces alkyl chain ordering around the rigid sterol ring and increases the cavity density within the hydrophilic region of both IPA bilayers. Furthermore, the enhanced alkyl chain ordering and the membrane deformation energy induced by cholesterol increase the permeation free energy penalty. In contrast, cholesterol has minor effects on the water local diffusivities within IPA membranes. Overall, the cholesterol reduces the water permittivity of rigid IPA membranes due to the synergistic effects of increased alkyl chain ordering and enhanced membrane mechanical modulus. The results provide molecular insights into the effects of molecular packing and mechanical deformations on the water permittivity of biomimetic IPA membranes, which is critical for designing IPA vesicular carriers.
Keywords: biomimetic membrane; cholesterol; ion pair amphiphile; molecular dynamics; water permeation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







References
-
- Yadav D., Sandeep K., Pandey D., Dutta R.K. Liposomes for Drug Delivery. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2017;7:276. doi: 10.4172/2155-952X.1000276. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

