A Novel AURKA Mutant-Induced Early-Onset Severe Hepatocarcinogenesis Greater than Wild-Type via Activating Different Pathways in Zebrafish
- PMID: 31269749
- PMCID: PMC6678475
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11070927
A Novel AURKA Mutant-Induced Early-Onset Severe Hepatocarcinogenesis Greater than Wild-Type via Activating Different Pathways in Zebrafish
Abstract
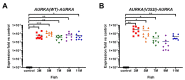
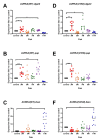
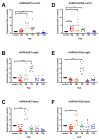
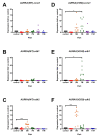
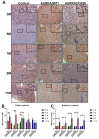
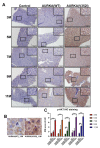
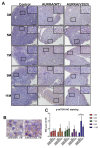
Aurora A kinase (AURKA) is an important regulator in mitotic progression and is overexpressed frequently in human cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Many AURKA mutations were identified in cancer patients. Overexpressing wild-type Aurka developed a low incidence of hepatic tumors after long latency in mice. However, none of the AURKA mutant animal models have ever been described. The mechanism of mutant AURKA-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis is still unclear. A novel AURKA mutation with a.a.352 Valine to Isoleucine (V352I) was identified from clinical specimens. By using liver-specific transgenic fish overexpressing both the mutant and wild-type AURKA, the AURKA(V352I)-induced hepatocarcinogenesis was earlier and much more severe than wild-type AURKA. Although an increase of the expression of lipogenic enzyme and lipogenic factor was observed in both AURKA(V352I) and AURKA(WT) transgenic fish, AURKA(V352I) has a greater probability to promote fibrosis at 3 months compared to AURKA(WT). Furthermore, the expression levels of cell cycle/proliferation markers were higher in the AURKA(V352I) mutant than AURKA(WT) in transgenic fish, implying that the AURKA(V352I) mutant may accelerate HCC progression. Moreover, we found that the AURKA(V352I) mutant activates AKT signaling and increases nuclear β-catenin, but AURKA(WT) only activates membrane form β-catenin, which may account for the differences. In this study, we provide a new insight, that the AURKA(V352I) mutation contributes to early onset hepatocarcinogenesis, possibly through activation of different pathways than AURKA(WT). This transgenic fish may serve as a drug-screening platform for potential precision medicine therapeutics.
Keywords: AKT signaling pathway; Aurora A kinase (AURKA); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); zebrafish; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
AURKA governs self-renewal capacity in glioma-initiating cells via stabilization/activation of β-catenin/Wnt signaling.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Sep;11(9):1101-11. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0044. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23761169
-
Aurora kinase A mediates c-Myc's oncogenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Nov;54(11):1467-79. doi: 10.1002/mc.22223. Epub 2014 Oct 4. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 25284017
-
SMAD4 suppresses AURKA-induced metastatic phenotypes via degradation of AURKA in a TGFβ-independent manner.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Dec;12(12):1779-95. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0191. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25061104
-
The ncRNA-AURKA Interaction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insights into Oncogenic Pathways, Therapeutic Opportunities, and Future Challenges.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 6;14(11):1430. doi: 10.3390/life14111430. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39598228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling as potential therapeutic targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1142-1149. doi: 10.1177/1535370217705865. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28429652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A gene module identification algorithm and its applications to identify gene modules and key genes of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 9;11(1):5517. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84837-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33750838 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Engineering of Zebrafish in Cancer Research.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;12(8):2168. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082168. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MCM4 as Potential Metastatic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 18;15(12):1555. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121555. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564876 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 12;10(6):898. doi: 10.3390/biom10060898. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32545625 Free PMC article.
-
Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan Prevents Radiation-Induced Fibrosis and Secondary Tumors in a Zebrafish Model.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 18;12(6):1608. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061608. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32570707 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

