HIV Epidemiology and Prevention in Southwestern China: Trends from 1996-2017
- PMID: 31269884
- PMCID: PMC6806534
- DOI: 10.2174/1570162X17666190703163838
HIV Epidemiology and Prevention in Southwestern China: Trends from 1996-2017
Abstract
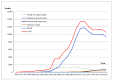
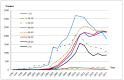
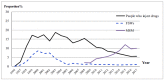
The aim of this review is to describe long-term HIV epidemiology and prevention trends in Guangxi, a provincial-level region located along a major drug trafficking corridor in southwestern China. Between 1996 and 2006, HIV transmission in Guangxi was primarily fueled by Injection Drug Use (IDU). Since 2006, heterosexual sex has become the dominant mode of HIV transmission, followed by drug injection. Moreover, older, heterosexual adults appear to be at increased risk for HIV. The vast majority of new HIV cases are attributed to local HIV subtypes already circulating within Guangxi (93%), though imported subtypes are associated with younger age groups. Since 2011, HIV incidence in Guangxi has stabilized, due in part to HIV prevention efforts that include expanded HIV testing, antiretroviral treatment, and other intervention measures. Between 1996 and 2017, Guangxi, China experienced dramatic changes in the primary HIV transmission mode and at-risk age group. Due in part to local and National AIDS control and prevention campaigns, HIV incidence trends in Guangxi no longer appear to be increasing.
Keywords: HIV; antiretroviral therapy; injection drug use; prevention; sexual intercourse; transmission..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Characteristics of newly reported HIV/AIDS cases with non-marital or non-commercial heterosexual transmission in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2015-2018].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 10;41(4):537-541. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190625-00467. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32344478 Chinese.
-
[Epidemiological characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2010-2017].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Mar 10;40(3):315-321. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.011. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30884610 Chinese.
-
Disparities in HIV and syphilis prevalence and risk factors between older male clients with and without steady sex partners in southwestern rural China.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Apr 12;17(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2367-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28403825 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS in east Africa: challenges and possibilities for prevention and control.East Afr Med J. 1996 Jan;73(1):13-9. East Afr Med J. 1996. PMID: 8625855 Review.
-
Microbicides-emerging essential pillars of comprehensive HIV/AIDS prevention.Ethiop Med J. 2006 Oct;44(4):405-15. Ethiop Med J. 2006. PMID: 17370443 Review.
Cited by
-
Interventions to improve the HIV continuum of care in China.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2019 Dec;16(6):448-457. doi: 10.1007/s11904-019-00469-y. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2019. PMID: 31776975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Young MSM changed temporal HIV-1 epidemic pattern in Heilongjiang Province, China.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 25;13:1028383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1028383. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36504809 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a Novel In-house HIV-1 Genotype Drug Resistance Assay using Clinical Samples in China.Curr HIV Res. 2022;20(1):32-41. doi: 10.2174/1570162X19666210910144433. Curr HIV Res. 2022. PMID: 34515004 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Delayed and Late Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy Among Patients With HIV in Beijing, China, 2010-2020.Int J Public Health. 2023 Jun 21;68:1605824. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1605824. eCollection 2023. Int J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37416802 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission network and phylogenetic analysis reveal older male-centered transmission of CRF01_AE and CRF07_BC in Guangxi, China.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023 Dec;12(1):2147023. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2147023. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023. PMID: 36369697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Kl K.L., Ma S.J. Epidemiology of HIV in China. BMJ. 2002;324(7341):803–804. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.324.7341.803]. [PMID: 11934762]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS Task Force on Drug Use and HIV. Drug use and HIV vulnerability: policy research study in Asia. Bangkok: UNAIDS Asia Pacific Intercountry Team; 2000.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime Global illicit drug trends. 2003 http://www.unodc.org
-
- Lowinger P. The solution to narcotic addiction in the People’s Republic of China. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1977;4(2):165–178. [http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00952997709002758]. [PMID: 347925]. - PubMed
-
- Thomas J. HIV / AIDS in China: Migrant population, drug injection responsible for increased transmission. AIDSlink. 1998;(49):12–14. [PMID: 12293301]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical