Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Controlled Study in Patients with Low Back Pain - Sciatica
- PMID: 31269891
- PMCID: PMC7132032
- DOI: 10.2174/1871527318666190703110036
Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Controlled Study in Patients with Low Back Pain - Sciatica
Abstract
Background: Despite being widely prescribed, relatively few controlled trials have been conducted on the class of neurotrophic/antinociceptive nutraceuticals. While performing a search in the literature, we came across an old registration study on micronized palmitoylethanolamide in patients with low back pain - sciatica by Guida and colleagues.
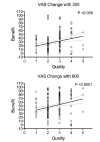
Methods: We contacted the authors of the article and obtained all the original material, which allowed us to reanalyze the study. We assessed its clinical relevance by calculating the numbers needed to treat for pain (visual analog scale) and function (Roland-Morris Questionnaire). After excluding patients for whom the information available was insufficient, we assigned each patient to one of the five categories of increasing probability of neuropathic pain: pure lumbago, lumbago with projecting pain to surrounding regions (e.g. gluteus or groin), lumbago with projecting pain to the thigh or leg, pure sciatica and radiculopathy, and investigated any correlations (Spearman) between the improvement in pain and function with these five classes.
Results: Compared with placebo, palmitoylethanolamide 600 mg/die yielded a number needed to treat of 1.7 (95% confidence interval: 1.4-2) for pain, and 1.5 (95% confidence interval: 1.4-1.7) for function. The correlation between the five categories was highly significant for pain relief (P <0.0001), though not significant for reduced dysfunction.
Conclusion: Palmitoylethanolamide was extremely effective on pain and function in a large cohort of patients with low back pain - sciatica. Although, the multiple mechanisms of action of palmitoylethanolamide are ideal for mixed pain conditions such as low back pain - sciatica, the correlation between pain relief and the likelihood of neuropathic pain suggests that this drug exerts a predominant action on the neuropathic pain component.
Keywords: Micronized palmitoylethanolamide; NSAIDs; low back pain; mixed pain; neuropathic pain; nutraceuticals; placebo..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
References
-
- Papanas N., Ziegler D. Efficacy of α-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014;15(18):2721–2731. - PubMed
-
- Skaper S.D., Facci L., Fusco M., et al. Palmitoylethanolamide, a naturally occurring disease-modifying agent in neuropathic pain. Inflammopharmacology. 2014;22(2):79–94. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10787-013-0191-7]. [PMID: 24178954]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

