[Identification of differentially expressed genes between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma using transcriber signature analysis]
- PMID: 31270041
- PMCID: PMC6743921
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.06.03
[Identification of differentially expressed genes between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma using transcriber signature analysis]
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) with bioinformatics analysis and search for potential biomarkers for clinical diagnosis of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: The gene expression profiling datasets of LUAD and LUSC were acquired. The transcriptome differences between LUAD and LUSC were identified using R language processing and t-test analysis. The differential expressions of the genes were shown by Venn diagram. The DEGs identified by GEO2R were analyzed with DAVID and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) to identify the signaling pathways and biomarkers that could be used for differential diagnosis of LUAD and LUSC. The TCGA data and the biomarker expression data from clinical lung cancer samples were used to verify the differential expressions of the Osteoarthritis pathway and LXR/RXR between LUAD and LUSC. We further examined the differential expressions of miR-181 and its two target genes, WNT5A and MBD2, in 23 clinical specimens of lung squamous cell carcinoma and the paired adjacent tissues.
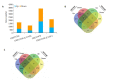
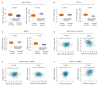
Results: GEO data analysis identified 851 DEGs (including 276 up-regulated and 575 down-regulated genes) in LUAD and 885 DEGs (including 406 up-regulated and 479 down-regulated genes) in LUSC. DAVID and IPA analysis revealed that leukocyte migration and inflammatory responses were more abundant in LUAD than in LUSC. Osteoarthritis pathway was inhibited in LUAD and activated in LUSC. IPA analysis showed that transcription factors (GATA4, RELA, YBX1, TP63 and MBD2), cytokines (WNT5A and IL1A) and microRNAs (miR-34a, miR-181b and miR-15a) differed significantly between LUAD and LUSC. miR-34a with IL-1A, miR-15a with YBX1, and miR-181b with WNT5A and MBD2 could serve as the paired microRNA and mRNA targets for differential diagnosis of NSCLC subtypes. Analysis of the clinical samples showed an increased expression of miR-181b-5p and the down-regulation of WNT5A, which could be used as molecular markers for the diagnosis of LUSC.
Conclusions: Through transcriptome analysis, we identified candidate genes, paired microRNAs and pathways for differentiating LUAD and LUSC, and they can provide novel differential diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for LUAD and LUSC.
目的: 对非小细胞肺癌两种亚型肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的基因差异表达进行生物信息学分析,寻找非小细胞肺癌潜在的生物学标志物运用于临床诊断,进而提高患者生存率。
方法: 获取肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的基因表达谱分析数据集,使用R语言处理,t检验分析鉴定肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌之间的转录组差异,并通过维恩图显示所鉴定的基因差异表达。从GEO获得差异表达的基因,用DAVID及IPA进行分析,进一步确定潜在可用于鉴别肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的几种信号通路和生物标记。利用TCGA数据和临床肺癌样本中的生物标记表达,验证Osteoarthritis pathway和LXR/RXR分别在肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的基因差异表达;挑选miR-181b-5p及其靶基因WNT5A和MBD2进行验证,收集23例肺鳞癌患者的肺肿瘤组织(23例肿瘤组织,实验组)及其邻近肺组织(23例癌旁肺组织,对照组),检测miR-181b-5p和其靶基因WNT5A和MBD2的表达差异用于鉴别肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌。
结果: GEO数据分析结果揭示肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的差异表达基因:肺腺癌中有851个DEGs(276个上调,575个下调),而肺鳞状细胞癌中有885个DEGs(406个上调,479个下调)。DAVID和IPA分析差异表达基因结果显示,白细胞迁移和炎症反应在肺腺癌中比肺鳞状细胞癌富集程度更高,Osteoarthritis pathway在肺腺癌中是抑制状态,而在肺鳞状细胞癌中显示是激活状态。IPA对重要转录因子、细胞因子和miRNA的分析结果显示肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌之间的区别主要是:转录因子(GATA4,RELA,YBX1,TP63和MBD2);细胞因子(WNT5A和IL-1A)和microRNA(miR-34a,miR-181b和miR-15a)。其中miR-34a和IL-1A、miR-15a和YBX1、miR-181b和WNT5A和MBD2可作为鉴别非小细胞肺癌亚型的成对microRNA和mRNA靶点。临床样本实验结果支持miR-181b-5p的表达上升和WNT5A的表达下调可视为诊断肺鳞状细胞癌的分子标记物。
结论: 通过对转录组数据分析,发现了肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌的候选基因、成对的microRNA鉴别肺腺癌和肺鳞状细胞癌,为其鉴别诊断和治疗提供了新的思路。
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma; lung squamous cell carcinoma; mRNA; microRNAs; transcriptome signature.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Feb;35(2):e23588. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23588. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 32965722 Free PMC article.
-
Use of four genes in exosomes as biomarkers for the identification of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):249. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12510. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33664813 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA expression profiling in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell lung carcinoma reveals both common and specific deregulated microRNAs.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Aug 19;101(33):e30027. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030027. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35984198 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of GLUT1 on the Survival Rate and Immune Cell Infiltration of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta and Bioinformatics Analysis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(2):223-238. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210708115406. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34238200 Review.
-
Differences between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma: Driver genes, therapeutic targets, and clinical efficacy.Genes Dis. 2024 Jul 11;12(3):101374. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101374. eCollection 2025 May. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 40083325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bjorkqvist AM, Husgafvel-Pursiainen K, Anttila S, et al. DNA gains in 3q occur frequently in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, but not in adenocarcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998;22(1):79–82. - PubMed
-
- Cooper WA, Lam DC, O'toole SA, et al. Molecular biology of lung cancer. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_89f8e87237faaa.... J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(5):S479–90. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
