NK cells switch from granzyme B to death receptor-mediated cytotoxicity during serial killing
- PMID: 31270246
- PMCID: PMC6719417
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20181454
NK cells switch from granzyme B to death receptor-mediated cytotoxicity during serial killing
Abstract
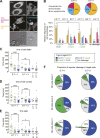
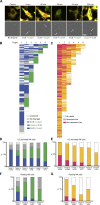
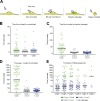
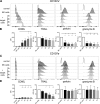
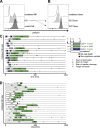
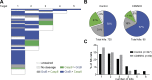
NK cells eliminate virus-infected and tumor cells by releasing cytotoxic granules containing granzyme B (GrzB) or by engaging death receptors that initiate caspase cascades. The orchestrated interplay between both cell death pathways remains poorly defined. Here we simultaneously measure the activities of GrzB and caspase-8 in tumor cells upon contact with human NK cells. We observed that NK cells switch from inducing a fast GrzB-mediated cell death in their first killing events to a slow death receptor-mediated killing during subsequent tumor cell encounters. Target cell contact reduced intracellular GrzB and perforin and increased surface-CD95L in NK cells over time, showing how the switch in cytotoxicity pathways is controlled. Without perforin, NK cells were unable to perform GrzB-mediated serial killing and only killed once via death receptors. In contrast, the absence of CD95 on tumor targets did not impair GrzB-mediated serial killing. This demonstrates that GrzB and death receptor-mediated cytotoxicity are differentially regulated during NK cell serial killing.
© 2019 Prager et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of the BCL2/adenovirus E1B-19K protein-interacting protein 2 (BNIP-2) as a granzyme B target during human natural killer cell-mediated killing.Biochem J. 2010 Nov 1;431(3):423-31. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091073. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20704564
-
Imaging burst kinetics and spatial coordination during serial killing by single natural killer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 16;110(16):6488-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221312110. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23576740 Free PMC article.
-
Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC) mimetic potentiates tumor susceptibility toward natural killer cell-mediated killing.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Mar;55(3):645-51. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.807925. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 23697877
-
New mechanism of organophosphorus pesticide-induced immunotoxicity.J Nippon Med Sch. 2007 Apr;74(2):92-105. doi: 10.1272/jnms.74.92. J Nippon Med Sch. 2007. PMID: 17507786 Review.
-
Mechanisms of natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Jun;105(6):1319-1329. doi: 10.1002/JLB.MR0718-269R. Epub 2019 May 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 31107565 Review.
Cited by
-
Arenavirus Induced CCL5 Expression Causes NK Cell-Mediated Melanoma Regression.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01849. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973762 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin signaling in the regulation of natural killer cells biology in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1449441. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449441. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39380989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Killer-Based Therapy: A Prospective Thought for Cancer Treatment Related to Diversified Drug Delivery Pathways.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 14;16(7):939. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070939. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death, therapeutics, and the immune response in cancer.Trends Cancer. 2023 May;9(5):381-396. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.02.001. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Trends Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36841748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vδ2 T-Cells Kill ZIKV-Infected Cells by NKG2D-Mediated Cytotoxicity.Microorganisms. 2019 Sep 12;7(9):350. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7090350. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31547470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backes C.S., Friedmann K.S., Mang S., Knörck A., Hoth M., and Kummerow C.. 2018. Natural killer cells induce distinct modes of cancer cell death: Discrimination, quantification, and modulation of apoptosis, necrosis, and mixed forms. J. Biol. Chem. 293:16348–16363. 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004549 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barry M., Heibein J.A., Pinkoski M.J., Lee S.F., Moyer R.W., Green D.R., and Bleackley R.C.. 2000. Granzyme B short-circuits the need for caspase 8 activity during granule-mediated cytotoxic T-lymphocyte killing by directly cleaving Bid. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:3781–3794. 10.1128/MCB.20.11.3781-3794.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

