Behavioural Responses of Unio tumidus Freshwater Mussels to Pesticide Contamination
- PMID: 31270566
- PMCID: PMC6731202
- DOI: 10.1007/s00244-019-00649-2
Behavioural Responses of Unio tumidus Freshwater Mussels to Pesticide Contamination
Abstract
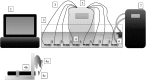
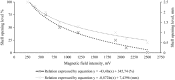
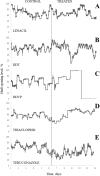
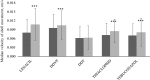
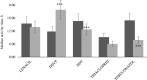
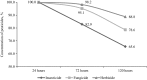
A pesticide is a chemical substance used for the disposal of pests, such as insects, weeds, invertebrates, or rodents. Pesticides interfere with the normal metabolism of the target species; however, some of them may inadvertently affect organisms other than those targeted. Increased quantities of pesticides in water disturb various ecological processes and may increase the mortality rate of various native species of flora and fauna. One of the groups of organisms that are at the greatest risk from the adverse effects of pesticides is the bivalves. This study was designed to assess the behavioural reaction of bivalves to widespread pesticides. As a representative example, the Polish native Unio tumidus (Philipsson 1788) was used. The study investigated different groups of toxic pesticides, such as herbicides (lenacil), insecticides (thiacloprid, DDT and dichlorvos), and fungicides (tebuconazole), in concentrations of 10 mg L-1. The results showed various behavioural reactions of bivalves to the pesticides. The most evident were activity time and shell opening rate. Moreover, as a result of DDVP contamination, effects were recorded in terms of shell opening level as well as rapid onset of death. Among the five analysed plant protection products, the most toxic was DDVP. Its presence caused adductor muscle paralysis in all analysed individuals. The least toxic pesticides were DDT and thiacloprid. A strong reaction to lenacil was observed especially in the shell opening rate. Tebuconazole caused significant reductions in activity. Despite the fact that the impact of pesticides on ecosystems is under regular observation, with the use of a wide range of scientific techniques, the use of bivalves was shown to have considerable potential for water quality monitoring.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Freshwater shrimps as sensitive test species for the risk assessment of pesticides in the tropics.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 May;25(14):13235-13243. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7451-1. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 27530199
-
Using species sensitivity distribution approach to assess the risks of commonly detected agricultural pesticides to Australia's tropical freshwater ecosystems.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2016 Feb;35(2):419-28. doi: 10.1002/etc.3199. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26260635
-
NiSO4 spill inflicts varying mortality between four freshwater mussel species (including protected Unio crassus Philipsson, 1788) in a western Finnish river.Environ Pollut. 2020 Jan;256:113402. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113402. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Environ Pollut. 2020. PMID: 31672360
-
Sublethal pesticide exposure in non-target terrestrial ecosystems: From known effects on individuals to potential consequences on trophic interactions and network functioning.Environ Res. 2024 Nov 1;260:119620. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119620. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 39032619 Review.
-
Twenty Years of Research in Ecosystem Functions in Aquatic Microbial Ecotoxicology.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2023 Sep;42(9):1867-1888. doi: 10.1002/etc.5708. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37401851 Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of Neonicotinoids on Molluscs: What We Know and What We Need to Know.Toxics. 2021 Jan 22;9(2):21. doi: 10.3390/toxics9020021. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 33499264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Freshwater Mussels as Sentinels for Safe Drinking Water Supply in Europe.ACS ES T Water. 2023 Nov 8;3(12):3730-3735. doi: 10.1021/acsestwater.3c00012. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. ACS ES T Water. 2023. PMID: 38094916 Free PMC article.
-
Lethal and Sub-lethal Implications of Sodium Chloride Exposure for Adult Unionid Mussel Species: Eurynia dilatata and Lasmigona costata.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2023 Jul;85(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00244-023-01006-0. Epub 2023 May 26. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37233741 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

