Characterization of a thaumarchaeal symbiont that drives incomplete nitrification in the tropical sponge Ianthella basta
- PMID: 31271506
- PMCID: PMC6790972
- DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.14732
Characterization of a thaumarchaeal symbiont that drives incomplete nitrification in the tropical sponge Ianthella basta
Abstract
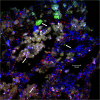
Marine sponges represent one of the few eukaryotic groups that frequently harbour symbiotic members of the Thaumarchaeota, which are important chemoautotrophic ammonia-oxidizers in many environments. However, in most studies, direct demonstration of ammonia-oxidation by these archaea within sponges is lacking, and little is known about sponge-specific adaptations of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA). Here, we characterized the thaumarchaeal symbiont of the marine sponge Ianthella basta using metaproteogenomics, fluorescence in situ hybridization, qPCR and isotope-based functional assays. 'Candidatus Nitrosospongia ianthellae' is only distantly related to cultured AOA. It is an abundant symbiont that is solely responsible for nitrite formation from ammonia in I. basta that surprisingly does not harbour nitrite-oxidizing microbes. Furthermore, this AOA is equipped with an expanded set of extracellular subtilisin-like proteases, a metalloprotease unique among archaea, as well as a putative branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter. This repertoire is strongly indicative of a mixotrophic lifestyle and is (with slight variations) also found in other sponge-associated, but not in free-living AOA. We predict that this feature as well as an expanded and unique set of secreted serpins (protease inhibitors), a unique array of eukaryotic-like proteins, and a DNA-phosporothioation system, represent important adaptations of AOA to life within these ancient filter-feeding animals.
© 2019 The Authors. Environmental Microbiology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Adams, M.D. , Wagner, L.M. , Graddis, T.J. , Landick, R. , Antonucci, T.K. , Gibson, A.L. , and Oxender, D.L. (1990) Nucleotide sequence and genetic characterization reveal six essential genes for the LIV‐I and LS transport systems of Escherichia coli . J Biol Chem 265: 11436–11443. - PubMed
-
- Ahlgren, N.A. , Chen, Y. , Needham, D.M. , Parada, A.E. , Sachdeva, R. , Trinh, V. , et al (2017) Genome and epigenome of a novel marine Thaumarchaeota strain suggest viral infection, phosphorothioation DNA modification and multiple restriction systems: genome and epigenome of a new marine thaumarchaeon. Environ Microbiol 19: 2434–2452. - PubMed
-
- Amano, F. , and Noda, T. (1995) Improved detection of nitric oxide radical (NO.) production in an activated macrophage culture with a radical scavenger, carboxy PTIO and Griess reagent. FEBS Lett 368: 425–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

