Individualized atrophy scores predict dementia onset in familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- PMID: 31272932
- PMCID: PMC6938544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.04.007
Individualized atrophy scores predict dementia onset in familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration
Abstract
Introduction: Some models of therapy for neurodegenerative diseases envision starting treatment before symptoms develop. Demonstrating that such treatments are effective requires accurate knowledge of when symptoms would have started without treatment. Familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration offers a unique opportunity to develop predictors of symptom onset.
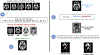
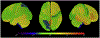
Methods: We created dementia risk scores in 268 familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration family members by entering covariate-adjusted standardized estimates of brain atrophy into a logistic regression to classify asymptomatic versus demented participants. The score's predictive value was tested in a separate group who were followed up longitudinally (stable vs. converted to dementia) using Cox proportional regressions with dementia risk score as the predictor.
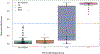
Results: Cross-validated logistic regression achieved good separation of asymptomatic versus demented (accuracy = 90%, SE = 0.06). Atrophy scores predicted conversion from asymptomatic or mildly/questionably symptomatic to dementia (HR = 1.51, 95% CI: [1.16,1.98]).
Discussion: Individualized quantification of baseline brain atrophy is a promising predictor of progression in asymptomatic familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration mutation carriers.
Keywords: Frontotemporal dementia; Genetics; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); TDP-43; Tau.
© 2019 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Figures


References
-
- Reiman EM. Alzheimer disease in 2016: Putting AD treatments and biomarkers to the test. Nat Rev Neurol 2017;13:74–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 AG061253/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG045333/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032306/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG045390/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS092089/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055121/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG063911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG023481/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG059891/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

