Carotid artery intima-media thickness, distensibility and elasticity: population epidemiology and concordance in Australian children aged 11-12 years old and their parents
- PMID: 31273013
- PMCID: PMC6624035
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020264
Carotid artery intima-media thickness, distensibility and elasticity: population epidemiology and concordance in Australian children aged 11-12 years old and their parents
Abstract
Objectives: To describe a well-established marker of cardiovascular risk, carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and related measures (artery distensibility and elasticity) in children aged 11-12 years old and mid-life adults, and examine associations within parent-child dyads.
Design: Cross-sectional study (Child Health CheckPoint), nested within a prospective cohort study, the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children (LSAC).
Setting: Assessment centres in seven Australian major cities and eight selected regional towns, February 2015 to March 2016.
Participants: Of all participating CheckPoint families (n=1874), 1489 children (50.0% girls) and 1476 parents (86.8% mothers) with carotid IMT data were included. Survey weights and methods were applied to account for LSAC's complex sample design and clustering within postcodes and strata.
Outcome measures: Ultrasound of the right carotid artery was performed using standardised protocols. Primary outcomes were mean and maximum far-wall carotid IMT, quantified using semiautomated edge detection software. Secondary outcomes were carotid artery distensibility and elasticity. Pearson's correlation coefficients and multivariable linear regression models were used to assess parent-child concordance. Random effects modelling on a subset of ultrasounds (with repeated measurements) was used to assess reliability of the child carotid IMT measure.
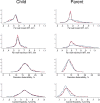
Results: The average mean and maximum child carotid IMT were 0.50 mm (SD 0.06) and 0.58 mm (SD 0.05), respectively. In adults, average mean and maximum carotid IMT were 0.57 mm (SD 0.07) and 0.66 mm (SD 0.10), respectively. Mother-child correlations for mean and maximum carotid IMT were 0.12 (95% CI 0.05 to 0.23) and 0.10 (95% CI 0.03 to 0.21), respectively. For carotid artery distensibility and elasticity, mother-child correlations were 0.19 (95% CI 0.10 to 0.25) and 0.11 (95% CI 0.02 to 0.18), respectively. There was no strong evidence of father-child correlation in any measure.
Conclusions: We provide Australian values for carotid vascular measures and report a modest mother-child concordance. Both genetic and environmental exposures are likely to contribute to carotid IMT.
Keywords: children; distensibility; epidemiological studies; inheritance patterns; intima-media thickness; reference values.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MW received support from Sandoz to present at a symposium outside the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular function and stiffness: population epidemiology and concordance in Australian children aged 11-12 years and their parents.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 4;9(Suppl 3):34-43. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020896. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31273014 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life: population epidemiology and concordance in Australian children aged 11-12 years and their parents.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 4;9(Suppl 3):157-164. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022398. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31273026 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between life-time exposure to ambient fine particulate matter and carotid artery intima-media thickness in Australian children aged 11-12 years.Environ Pollut. 2021 Dec 15;291:118072. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118072. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Environ Pollut. 2021. PMID: 34592695
-
[Intima media thickness of the carotid arteries: early pointer to arteriosclerosis and therapeutic endpoint].Ultraschall Med. 2003 Jun;24(3):162-74. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40058. Ultraschall Med. 2003. PMID: 12817310 Review. German.
-
Intima Media Thickness and Cognitive Function Among Adults: Meta-Analysis of Observational and Longitudinal Studies.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Mar;11(5):e021760. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.021760. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35179392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sonographic assessment of carotid intima-media thickness in healthy young Thai adults.Imaging Sci Dent. 2023 Dec;53(4):291-302. doi: 10.5624/isd.20230021. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Imaging Sci Dent. 2023. PMID: 38174040 Free PMC article.
-
Diet quality trajectories and cardiovascular phenotypes/metabolic syndrome risk by 11-12 years.Int J Obes (Lond). 2021 Jul;45(7):1392-1403. doi: 10.1038/s41366-021-00800-x. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Int J Obes (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33824404
-
Increased innate immune responses in adolescents with obesity and its relation to subclinical cardiovascular measures: An exploratory study.iScience. 2024 Apr 23;27(5):109762. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109762. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38741712 Free PMC article.
-
Population health bio-phenotypes in 11-12 year old children and their midlife parents: Growing Up in Australia's Child Health CheckPoint.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 4;9(Suppl 3):1-2. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030833. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31273011 Free PMC article.
-
Child Health CheckPoint: cohort summary and methodology of a physical health and biospecimen module for the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 4;9(Suppl 3):3-22. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020261. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31273012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naghavi M, Wang HD, Lozano R, et al. . Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015;385:117–71. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urbina EM, Williams RV, Alpert BS, et al. . Noninvasive assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in children and adolescents: recommendations for standard assessment for clinical research: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2009;54:919–50. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.192639 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
