Divergent Effects of Acute and Prolonged Interleukin 33 Exposure on Mast Cell IgE-Mediated Functions
- PMID: 31275312
- PMCID: PMC6593472
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01361
Divergent Effects of Acute and Prolonged Interleukin 33 Exposure on Mast Cell IgE-Mediated Functions
Abstract
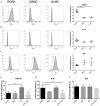
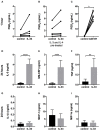
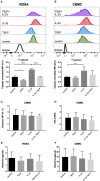
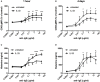
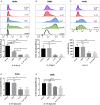
Background: Epithelial cytokines, including IL-33 and Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), have attracted interest because of their roles in chronic allergic inflammation-related conditions such as asthma. Mast cells are one of the major targets of IL-33, to which they respond by secreting cytokines. Most studies performed thus far have investigated the acute effects of IL-33 on mast cells. In the current study, we investigated how acute vs. prolonged exposure of mast cells to IL-33 and TSLP affects mediator synthesis and IgE-mediated activation. Methods: Human lung mast cells (HLMCs), cord blood-derived mast cells (CBMCs), and the ROSA mast cell line were used for this study. Receptor expression and the levels of mediators were measured after treatment with IL-33 and/or TSLP. Results: IL-33 induced the release of cytokines. Prolonged exposure to IL-33 increased while TSLP reduced intracellular levels of tryptase. Acute IL-33 treatment strongly potentiated IgE-mediated activation. In contrast, 4 days of exposure to IL-33 decreased IgE-mediated activation, an effect that was accompanied by a reduction in FcεRI expression. Conclusion: We show that IL-33 plays dual roles in mast cells, in which its acute effects include cytokine release and the potentiation of IgE-mediated degranulation, whereas prolonged exposure to IL-33 reduces IgE-mediated activation. We conclude that mast cells act quickly in response to the alarmin IL-33 to initiate an acute inflammatory response, whereas extended exposure to IL-33 during prolonged inflammation reduces IgE-mediated responses. This negative feedback effect suggests the presence of a novel regulatory pathway that modulates IgE-mediated human mast cell responses.
Keywords: FcεRI; IL-33; IgE; TSLP; mast cells.
Figures

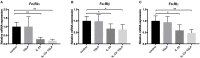
Similar articles
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-induced interleukin-17A is involved in the development of IgE-mediated atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice.Immunology. 2015 Dec;146(4):568-81. doi: 10.1111/imm.12528. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 26310839 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanin CD151 Is a Negative Regulator of FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation.J Immunol. 2015 Aug 15;195(4):1377-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302874. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26136426 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Human Basophils by A549 Lung Epithelial Cells Reveals a Novel IgE-Dependent Response Independent of Allergen.J Immunol. 2017 Aug 1;199(3):855-865. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700055. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28652400 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in mast cell functions.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 May 5;778:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.04.047. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26051792 Review.
-
Beyond IgE: Alternative Mast Cell Activation Across Different Disease States.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1498. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041498. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Approaches in the Inhibition of IgE-Induced Mast Cell Reactivity in Food Allergy.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:613461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.613461. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergism between IL-33 and MRGPRX2/FcεRI Is Primarily Due to the Complementation of Signaling Modules, and Only Modestly Supplemented by Prolonged Activation of Selected Kinases.Cells. 2023 Nov 24;12(23):2700. doi: 10.3390/cells12232700. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067128 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Strategies to Target Mast Cells in Disease.J Innate Immun. 2021;13(3):131-147. doi: 10.1159/000513582. Epub 2021 Feb 12. J Innate Immun. 2021. PMID: 33582673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Interferes with the Apoptosis of Human Skin Mast Cells by a Dual Strategy Involving STAT5/Mcl-1 and JNK/Bcl-xL.Cells. 2019 Aug 5;8(8):829. doi: 10.3390/cells8080829. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31387206 Free PMC article.
-
GM-CSF drives dysregulated hematopoietic stem cell activity and pathogenic extramedullary myelopoiesis in experimental spondyloarthritis.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 9;11(1):155. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13853-4. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31919358 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

