Antibody Specificity Following a Recent Bordetella pertussis Infection in Adolescence Is Correlated With the Pertussis Vaccine Received in Childhood
- PMID: 31275314
- PMCID: PMC6592373
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01364
Antibody Specificity Following a Recent Bordetella pertussis Infection in Adolescence Is Correlated With the Pertussis Vaccine Received in Childhood
Abstract
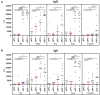
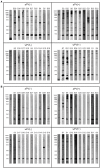
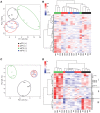
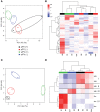
Bordetella (B.) pertussis resurgence affects not only the unvaccinated, but also the vaccinated population. Different vaccines are available, however, it is currently unknown whether the type of childhood vaccination has an influence on antibody responses following a B. pertussis infection later in life. Therefore, the study aim was to profile serum antibody responses in young adults with suspected B. pertussis infections, immunized during childhood with either whole-cell (wPV) or monocomponent acellular pertussis (aPV) vaccines. Serum anti-pertussis toxin (PTx) IgG antibody levels served as an indicator for a recent B. pertussis infection. Leftover sera from a diagnostic laboratory from 36 Danish individuals were included and divided into four groups based on immunization background (aPV vs. wPV) and serum anti-PTx IgG levels (- vs. +). Pertussis-specific IgG/IgA antibody levels and antigen specificity were determined by using multiplex immunoassays (MIA), one- and two-dimensional immunoblotting (1 & 2DEWB), and mass spectrometry. Besides enhanced anti-PTx levels, wPV(+) and aPV(+) groups showed increased IgG and IgA levels against pertactin, filamentous hemagglutinin, fimbriae 2/3, and pertussis outer membrane vesicles (OMV). In the wPV(-) and aPV(-) groups, only low levels of anti-OMV antibodies were detected. 1DEWB demonstrated that antibody patterns differed between groups but also between individuals with the same immunization background and anti-PTx levels. 2DWB analysis for serum IgG revealed 133 immunogenic antigens of which 40 were significantly different between groups allowing to differentiate wPV(+) and aPV(+) groups. Similarly, for serum IgA, 7 of 47 immunogenic protein spots were significantly different. This study demonstrated that B. pertussis infection-induced antibody responses were distinct on antigen level between individuals with either wPV or aPV immunization background. Importantly, only 2DEWB and not MIA could detect these differences indicating the potential of this method. Moreover, in individuals immunized with an aPV containing only PTx in childhood, the infection-induced antibody responses were not limited to PTx alone.
Keywords: 2-dimensional electrophoresis (2DE); Bordetella pertussis; acellular pertussis vaccine; antibody specificity; infection-induced response; pertussis toxin (PTx); vaccination; whole-cell pertussis vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of IgA anti-PT and IgG anti-ACT reflex testing to improve Bordetella pertussis serodiagnosis in recently vaccinated subjects.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 May;26(5):645.e1-645.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 31610300
-
Antibody responses to pertussis toxin display different kinetics after clinical Bordetella pertussis infection than after vaccination with an acellular pertussis vaccine.J Med Microbiol. 2010 Sep;59(Pt 9):1029-1036. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.020826-0. Epub 2010 May 27. J Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20508003
-
Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of an Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Candidate in a Mice Model.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Jul 27;23(4):422-436. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v23i4.16216. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39549295
-
Immunologic and epidemiologic experience of vaccination with a monocomponent pertussis toxoid vaccine.Pediatrics. 2001 Dec;108(6):E115. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.6.e115. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11731642 Review.
-
Pertussis Prevention: Reasons for Resurgence, and Differences in the Current Acellular Pertussis Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 3;10:1344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01344. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31333640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro alternative for reactogenicity assessment of outer membrane vesicle based vaccines.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 4;13(1):12675. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39908-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37542099 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal immunization with outer membrane vesicle pertussis vaccine confers broad protection through mucosal IgA and Th17 responses.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;10(1):7396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63998-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32355188 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of Multiplex Assays for Mouse and Human IgG and IgA to Neisseria gonorrhoeae Antigens.J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 16;230(4):852-856. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae153. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38526341 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella pertussis whole cell immunization protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Nov 10;7(1):143. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00562-1. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36357402 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Virulence Proteins in Protection Conferred by Bordetella pertussis Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;8(3):429. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030429. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Pertussis. In: ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2016. Stockholm:ECDC; (2018).
-
- Thierry-Carstensen B, Dalby T, Stevner MA, Robbins JB, Schneerson R, Trollfors B. Experience with monocomponent acellular pertussis combination vaccines for infants, children, adolescents and adults–a review of safety, immunogenicity, efficacy and effectiveness studies and 15 years of field experience. Vaccine. (2013) 31:5178–91. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.034 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

