Antimetastasis Effect of Astragalus membranaceus- Curcuma zedoaria via β-Catenin Mediated CXCR4 and EMT Signaling Pathway in HCT116
- PMID: 31275425
- PMCID: PMC6582911
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9692350
Antimetastasis Effect of Astragalus membranaceus- Curcuma zedoaria via β-Catenin Mediated CXCR4 and EMT Signaling Pathway in HCT116
Abstract
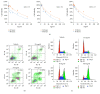
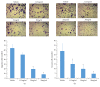
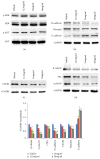
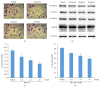
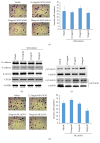
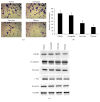
Astragalus membranaceus and Curcuma zedoaria, two traditional Chinese medicines, are widely used together in colorectal cancer adjuvant treatment. Many different mechanisms should be involved in the benefit effect of Astragalus membranaceus and Curcuma zedoaria. In this study, we established that the combined extract from Astragalus membranaceus and Curcuma zedoaria (HQEZ) decreased the metastasis ability in colorectal cancer cells (HCT116, a cell line of colorectal carcinoma established from Homo sapiens) in vitro, and the treatment induced the downregulation of EMT signal and decreased CXCR4 expression and the level of β-catenin. Overexpression of CXCR4 and the administration of the agonist and inhibitor to β-catenin signal pathway were used to explore the mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus and Curcuma zedoaria in colorectal cancer treatment. The data demonstrated that HQEZ increased the phosphorylation of β-catenin which related to the degradation of β-catenin, and it induced the downregulation of EMT signal and CXCR4. It meant that the influence of β-catenin should be a key event in the antimetastasis effects of Astragalus membranaceus-Curcuma zedoaria in colorectal cancer model. These findings revealed the potential effect and mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus-Curcuma zedoaria in colorectal cancer treatment and provided insight for optimization of the usage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi) and Rhizoma curcumae (Ezhu) decoction suppresses colorectal cancer via downregulation of Wnt5/β-Catenin signal.Chin Med. 2022 Jan 6;17(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00564-6. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 34991661 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker identification and pathway analysis of Astragalus membranaceus and Curcuma zedoaria couplet medicines on adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats based on metabolomics.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1103527. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1103527. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089928 Free PMC article.
-
Metabonomics study on orthotopic transplantion mice model of colon cancer treated with Astragalus membranaceus-Curcuma wenyujin in different proportions via UPLC-Q-TOF/MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021 Jan 30;193:113708. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113708. Epub 2020 Oct 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021. PMID: 33129117
-
Research progress of Astragalus membranaceus in treating peritoneal metastatic cancer.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;305:116086. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116086. Epub 2022 Dec 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36587879 Review.
-
Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Traditional Uses of Curcuma spp. and Pharmacological Profile of Two Important Species (C. longa and C. zedoaria): A Review.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(8):871-935. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190402163940. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30947655 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect and Related Mechanism of Action of Astragalus Compatible with Curcumin against Colon Cancer Metastasis in Mice.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022 Jun 10;2022:9578307. doi: 10.1155/2022/9578307. eCollection 2022. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022. Retraction in: Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2023 Aug 16;2023:9793254. doi: 10.1155/2023/9793254. PMID: 35721822 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mechanism of hedysari radix praeparata cum melle and curcumae rhizoma herb pair in colitis-associated colorectal cancer through the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway: an investigation in vivo and in vitro.Front Chem. 2025 May 8;13:1551722. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1551722. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40405896 Free PMC article.
-
Tianma Granules Alleviate AOM/DSS-Induced Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(15):e70772. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70772. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40785041 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Post-Translational Modifications in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;16(3):652. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030652. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge-Curcuma aromatica Salisb. suppresses growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization via a Sp1/ZFAS1/miR-153-3p/CCR5 regulatory axis.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Aug;38(4):679-697. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09679-w. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35072892
References
-
- Chen M., May B. H., Zhou I. W., Sze D. M.-Y., Xue C. C., Zhang A. L. Oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy combined with traditional medicines for neutropenia in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the contributions of specific plants. Critical Review in Oncology/Hematology. 2016;105:18–34. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chien T., Liu C., Lu R., Kuo C., Lin Y., Hsu C. Therapeutic efficacy of Traditional Chinese medicine, “Kuan-Sin-Yin”, in patients undergoing chemotherapy for advanced colon cancer – a controlled trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2016;29:204–212. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2016.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

