Frequent Sips of the Water for the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Induced Refractory Cough: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 31275669
- PMCID: PMC6582892
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9205259
Frequent Sips of the Water for the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Induced Refractory Cough: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background: Chronic cough is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The role of gastroenterologist in the management of the chronic cough is to identify and manage GERD. Ineffective esophageal motility is often associated with GERD induced cough. Chronic cough is often refractory to medical and surgical management despite adequate acid control. Unresponsiveness warrants a thorough pulmonary evaluation. The pathophysiology of refractory cough in these patients is poorly understood, and hence management is often challenging.
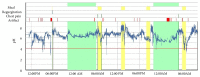
Case presentation: A 75-year-old woman from Ghana was evaluated for GERD associated chronic cough. A 48-hour ambulatory pH study revealed acid exposure of 4.9% and high-resolution manometry showed decreased lower esophageal sphincter pressure, an inadequate response to medical and surgical management of GERD. Postfundoplication ambulatory pH testing demonstrated well-controlled acid reflux but her cough still persisted. Repeat manometry showed an ineffective motility disorder (IEM). Taking frequent sips of water eventually resolved her chronic cough.
Conclusion: Frequent sips of water can be used in the management of the gastroesophageal reflux and ineffective motility induced cough. It results in increased esophageal clearance of acid, nonacid reflux, and ingested pharyngeal secretions, thus breaking the cycle of cough generated increased intra-abdominal pressure with reflux and more cough.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic cough: A possible mechanism elucidated by ambulatory pH-impedance-pressure monitoring.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Dec;31(12):e13707. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13707. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019. PMID: 31482661 Free PMC article.
-
[A study of esophageal function and reflux characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients presenting with chronic cough].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Nov;50(11):931-4. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22333125 Chinese.
-
A study on the esophageal dynamics in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and with refractory cough undergoing esophageal high-resolution manometry.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):9546-9553. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34540077 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal Motor Dysfunctions in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Therapeutic Perspectives.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Oct 30;25(4):499-507. doi: 10.5056/jnm19081. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019. PMID: 31587540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARE THE PERSISTENT SYMPTOMS TO PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR THERAPY DUE TO REFRACTORY GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE OR TO OTHER DISORDERS?Arq Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov;55Suppl 1(Suppl 1):85-91. doi: 10.1590/S0004-2803.201800000-48. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30304291 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources