Therapeutic hFIX Activity Achieved after Single AAV5-hFIX Treatment in Hemophilia B Patients and NHPs with Pre-existing Anti-AAV5 NABs
- PMID: 31276009
- PMCID: PMC6586596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.05.009
Therapeutic hFIX Activity Achieved after Single AAV5-hFIX Treatment in Hemophilia B Patients and NHPs with Pre-existing Anti-AAV5 NABs
Abstract
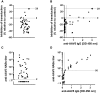
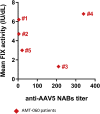
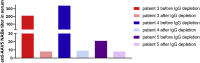
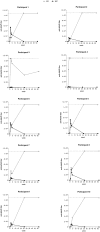
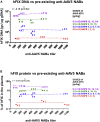
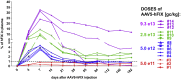
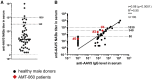
Currently, individuals with pre-existing neutralizing antibodies (NABs) against adeno-associated virus (AAV) above titer of 5 are excluded from systemic AAV-based clinical trials. In this study we explored the impact of pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs on the efficacy of AAV5-based gene therapy. AMT-060 (AAV5-human FIX) was evaluated in 10 adults with hemophilia B who tested negative for pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs using a GFP-based assay. In this study, using a more sensitive luciferase-based assay, we show that 3 of those 10 patients tested positive for anti-AAV5 NABs. However, no relationship was observed between the presence of pre-treatment anti-AAV5 NABs and the therapeutic efficacy of AMT-060. Further studies in non-human primates (NHPs) showed that AAV5 transduction efficacy was similar following AMT-060 treatment, irrespective of the pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs titers. We show that therapeutic efficacy of AAV5-mediated gene therapy was achieved in humans with pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs titers up to 340. Whereas in NHPs circulating human factor IX (hFIX) protein was achieved, at a level therapeutic in humans, with pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs up to 1030. Based on those results, no patients were excluded from the AMT-061 (AAV5-hFIX-Padua) phase IIb clinical trial (n = 3). All three subjects presented pre-existing anti-AAV5 NABs, yet had therapeutic hFIX activity after AMT-061 administration.
Keywords: AAV; FIX; NABs; anti-AAV NABs; gene therapy; hFIX; hemophilia.
Figures
References
-
- Hurlbut G.D., Ziegler R.J., Nietupski J.B., Foley J.W., Woodworth L.A., Meyers E., Bercury S.D., Pande N.N., Souza D.W., Bree M.P. Preexisting immunity and low expression in primates highlight translational challenges for liver-directed AAV8-mediated gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010;18:1983–1994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang H., Couto L.B., Patarroyo-White S., Liu T., Nagy D., Vargas J.A., Zhou S., Scallan C.D., Sommer J., Vijay S. Effects of transient immunosuppression on adenoassociated, virus-mediated, liver-directed gene transfer in rhesus macaques and implications for human gene therapy. Blood. 2006;108:3321–3328. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manno C.S., Pierce G.F., Arruda V.R., Glader B., Ragni M., Rasko J.J., Ozelo M.C., Hoots K., Blatt P., Konkle B. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat. Med. 2006;12:342–347. - PubMed
-
- Scallan C.D., Jiang H., Liu T., Patarroyo-White S., Sommer J.M., Zhou S., Couto L.B., Pierce G.F. Human immunoglobulin inhibits liver transduction by AAV vectors at low AAV2 neutralizing titers in SCID mice. Blood. 2006;107:1810–1817. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

