Multilayered Microfluidic Paper-Based Devices: Characterization, Modeling, and Perspectives
- PMID: 31276368
- PMCID: PMC7653499
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01112
Multilayered Microfluidic Paper-Based Devices: Characterization, Modeling, and Perspectives
Abstract
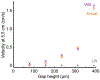
Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) are simple but powerful analytical tools that are gaining significant recent attention due to their many advantages over more traditional monitoring tools. These include being inexpensive, portable, pump-free, and having the ability to store reagents. One major limitation of these devices is slow flow rates, which are controlled by capillary action in the hydrophilic pores of cellulosic paper. Recent investigations have advanced the flow rates in μPADs through the generation of a gap or channel between two closely spaced paper sheets. This multilayered format has opened up μPADs to new applications and detection schemes, where large gap sizes (>300 μm) provide at least 169× faster flow rates than single-layer μPADs, but do not conform to established mathematical models for fluid transport in porous materials, such as the classic Lucas-Washburn equation. In the present study, experimental investigations and analytical modeling are applied to elucidate the driving forces behind the rapid flow rates in these devices. We investigate a range of hypotheses for the systems fluid dynamics and establish a theoretical model to predict the flow rate in multilayered μPADs that takes into account viscous dissipation within the paper. Device orientation, sample addition method, and the gap height are found to be critical concerns when modeling the imbibition in multilayered devices.
Figures
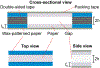
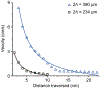

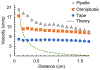
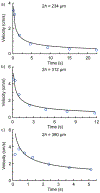
 ) correspond to the experimental values while the black line represents the model predictionl. The gap heights are (a) 234 μm, (b) 312 μm, and (c) 390 μm.
) correspond to the experimental values while the black line represents the model predictionl. The gap heights are (a) 234 μm, (b) 312 μm, and (c) 390 μm.Similar articles
-
Paper-Based Vertical Flow Assays for in Vitro Diagnostics and Environmental Monitoring.ACS Sens. 2025 May 23;10(5):3317-3339. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.5c00668. Epub 2025 May 15. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 40372939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-dimensional microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) for noninvasive testing: A review of structural design and applications.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 Sep 8;1321:342877. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342877. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39155092 Review.
-
Enzyme embedded microfluidic paper-based analytic device (μPAD): a comprehensive review.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2021 Nov;41(7):1046-1080. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1898327. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33730940 Review.
-
Rapid flow in multilayer microfluidic paper-based analytical devices.Lab Chip. 2018 Feb 27;18(5):793-802. doi: 10.1039/c7lc01300k. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 29431751 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for cancer biomarker detection: From 2D to 3D sensing systems.Talanta. 2023 May 15;257:124370. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124370. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 36858013 Review.
Cited by
-
Flow control in a laminate capillary-driven microfluidic device.Analyst. 2021 Mar 21;146(6):1932-1939. doi: 10.1039/d0an02279a. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Analyst. 2021. PMID: 33492316 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced capillary pumping using open-channel capillary trees with integrated paper pads.Phys Fluids (1994). 2023 Aug;35(8):082120. doi: 10.1063/5.0157801. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Phys Fluids (1994). 2023. PMID: 37675268 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic and Microscale Assays to Examine Regenerative Strategies in the Neuro Retina.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;11(12):1089. doi: 10.3390/mi11121089. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33316971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling Capillary Flow Rate on Lateral Flow Test Substrates by Tape.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 May 16;12(5):562. doi: 10.3390/mi12050562. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065694 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Pipetteless Paper-Based Analytical Devices with a Volume Gauge.ACS Omega. 2023 Mar 17;8(12):11213-11219. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08138. eCollection 2023 Mar 28. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37008150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization, W. H. World Health Organization Model List of Essential In Vitro Diagnostics; 16-20 April 2018, 2018.
-
- Gong MM; Sinton D, Turning the Page: Advancing Paper-Based Microfluidics for Broad Diagnostic Application. Chem. Rev 2017, 117 (12), 8447–8480. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y; Noviana E; Nguyen MP; Geiss BJ; Dandy DS; Henry CS, Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices: Emerging Themes and Applications. Anal. Chem 2017, 89 (1), 71–91. - PubMed
-
- Yamada K; Shibata H; Suzuki K; Citterio D, Toward practical application of paper-based microfluidics for medical diagnostics: state-of-the-art and challenges. Lab Chip 2017, 17 (7), 1206–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

