Quantum Chemical Modeling of the Photoinduced Activity of Multichromophoric Biosystems
- PMID: 31276384
- PMCID: PMC6716121
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00135
Quantum Chemical Modeling of the Photoinduced Activity of Multichromophoric Biosystems
Abstract
Multichromophoric biosystems represent a broad family with very diverse members, ranging from light-harvesting pigment-protein complexes to nucleic acids. The former are designed to capture, harvest, efficiently transport, and transform energy from sunlight for photosynthesis, while the latter should dissipate the absorbed radiation as quickly as possible to prevent photodamages and corruption of the carried genetic information. Because of the unique electronic and structural characteristics, the modeling of their photoinduced activity is a real challenge. Numerous approaches have been devised building on the theoretical development achieved for single chromophores and on model Hamiltonians that capture the essential features of the system. Still, a question remains: is a general strategy for the accurate modeling of multichromophoric systems possible? By using a quantum chemical point of view, here we review the advancements developed so far highlighting differences and similarities with the single chromophore treatment. Finally, we outline the important limitations and challenges that still need to be tackled to reach a complete and accurate picture of their photoinduced properties and dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



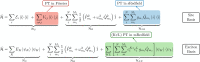
 . The GS energy Eg is safely assumed
to be zero.
. The GS energy Eg is safely assumed
to be zero.  and
and  represent, respectively,
nuclear momenta
and coordinates operators; gm are the coupling constants between nuclear and electronic
degrees of freedom (linear coupling). The perturbative terms (PT)
that enter in the various transport theories are highlighted in the
colored boxes.
represent, respectively,
nuclear momenta
and coordinates operators; gm are the coupling constants between nuclear and electronic
degrees of freedom (linear coupling). The perturbative terms (PT)
that enter in the various transport theories are highlighted in the
colored boxes.
References
-
- Fleming G. R. Subpicosecond Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1986, 37, 81–104. 10.1146/annurev.pc.37.100186.000501. - DOI
-
- Eads D.; Jean J.; Chan C.-K.; Mets L.; Alberte R.; Fleming G. Energy Transfer in Photosynthesis. Proc. of ICEET (Prague) 1990, 2, 64–68.
-
- Jimenez R.; Fleming G. R.. Ultrafast Spectroscopy of Excitation Transfer Dynamics in Biological Systems. In Femtochemistry and Femtobiology: Ultrafast Reaction Dynamics at Atomic-Scale Resolution; Proceedings of Nobel Symposium 101 V. Sundström, 1997, 701–723.
-
- Scholes G. D. Quantum-Coherent Electronic Energy Transfer: Did Nature Think of It First?. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2–8. 10.1021/jz900062f. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

