Propylthiouracil-induced organizing pneumonia: A case report
- PMID: 31277157
- PMCID: PMC6635233
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016284
Propylthiouracil-induced organizing pneumonia: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a common antithyroid drug which can treat hyperthyroidism effectively. PTU is, however, associated to multiple adverse effects. In rare case, PTU can cause interstitial pneumonia.
Patient concerns: A 40-year-old woman presented with dyspnea and was diagnosed with pulmonary infection at the first time. After the treatment with moxifloxacin, her symptoms still got worse.
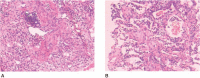
Diagnosis: The lung tissues biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of organizing pneumonia (OP) and the administration of PTU suggested the diagnosis of PTU-induced OP.
Intervention: Withdrawal of PTU and the administration of methylprednisolone.
Outcomes: The patient's symptoms relieved significantly 1 month later and lung computed tomography (CT) scan also demonstrated significant reduction of lung lesions.
Lessons: Here we report the first case of histologically confirmed OP induced by PTU and conduct a literature review of the cases of PTU-induced interstitial pneumonia. The awareness of PTU-induced OP can help physicians reduce the possibility of misdiagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nebesio TD, Eugster EA. Antithyroid drugs. N Engl J Med 2005;352:2246–7. - PubMed
-
- Miyazono K, Okazaki T, Uchida S, et al. Propylthiouracil-induced diffuse interstitial pneumonitis. Arch Intern Med 1984;144:1764–5. - PubMed
-
- Ohwada R, Kato K, Ohmori K, et al. A man with interstitial pneumonia due to propylthiouracil. Intern Med 2003;42:1026–30. - PubMed
-
- Ji YL, Chung JH, Lee YJ, et al. Propylthiouracil-induced nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Chest 2011;139:687–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

