Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study
- PMID: 31277204
- PMCID: PMC6651692
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20133267
Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study
Abstract
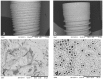
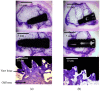
The surface modifications of titanium dental implants play important roles in the enhancement of osseointegration. The objective of the present study was to test two different implant surface treatments on a rabbit model to investigate the osseointegration. The tested surfaces were: a) acid-etched surface with sandblasting treatment (SA) and b) an oxidized implant surface (OS). The roughness was measured by an interferometeric microscope with white light and the residual stress of the surfaces was measured with X-ray residual stress Bragg-Bentano diffraction. Six New Zealand white rabbits were used for the in vivo study. Implants with the two different surfaces (SA and OS) were inserted in the femoral bone. After 12 weeks of implantation, histological and histomorphometric analyses of the blocks containing the implants and the surrounding bone were performed. All the implants were correctly implanted and no signs of infection were observed. SA and OS surfaces were both surrounded by newly formed trabeculae. Histomorphometric analysis revealed that the bone-implant contact % (BIC) was higher around the SA implants (53.49 ± 8.46) than around the OS implants (50.94 ± 16.42), although there were no significant statistical differences among them. Both implant surfaces (SA and OS) demonstrated a good bone response with significant amounts of newly formed bone along the implant surface after 12 weeks of implantation. These results confirmed the importance of the topography and physico-chemical properties of dental implants in the osseointegration.
Keywords: acid-etched surface; implant surface; osseointegration; oxidized surface; sandblasted surface; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Osseointegration of Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Implant Surfaces. A Histological and Histomorphometric Study in the Rabbit.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 7;22(16):8507. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168507. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445213 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the osseointegration of dental implants coated with calcium carbonate: an animal study.Int J Oral Sci. 2017 Sep;9(3):133-138. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2017.13. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Int J Oral Sci. 2017. PMID: 28452375 Free PMC article.
-
Osseointegration of Titanium Implants With Different Rough Surfaces: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in an Adult Minipig Model.Implant Dent. 2017 Jun;26(3):357-366. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000560. Implant Dent. 2017. PMID: 28234707
-
Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: current knowledge and open questions.Periodontol 2000. 2017 Feb;73(1):22-40. doi: 10.1111/prd.12179. Periodontol 2000. 2017. PMID: 28000277 Review.
-
Surface Modifications of Commercial Dental Implant Systems: An Overview.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2023;33(2):71-77. doi: 10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.2022042612. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2023. PMID: 36734929 Review.
Cited by
-
Laser Surface Modification of Powder Metallurgy-Processed Ti-Graphite Composite Which Can Enhance Cells' Osteo-Differentiation.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;14(20):6067. doi: 10.3390/ma14206067. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34683656 Free PMC article.
-
Workflow for Maxilla/Mandible Individual [Mai®] Implant by Integra Implants-How Individual Implants Are Manufactured.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):1773. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081773. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200237 Free PMC article.
-
Laser-Induced µ-Rooms for Osteocytes on Implant Surface: An In Vivo Study.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;12(23):4229. doi: 10.3390/nano12234229. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500852 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of enamel matrix derivatives and surface morphology of anodized titanium on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells sheet.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):1085-1096. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36915734 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of a Bacteriostatic Surface on ZrNb Alloy via Anodization in a Solution Containing Cu Nanoparticles.Materials (Basel). 2020 Sep 4;13(18):3913. doi: 10.3390/ma13183913. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32899716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berglundh T., Persson L., Klinge B. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002;29(Suppl. 3):197–212. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051X.29.s3.12.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Iezzi G., Scarano A., Di Stefano D., Arosio P., Doi K., Ricci L., Piattelli A., Perrotti V. Correlation between the bone density recorded by a computerized implant motor and by a histomorphometric analysis: A preliminary in vitro study on bovine ribs. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015;17:35–44. doi: 10.1111/cid.12121. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

