High Constitutive Cytokine Release by Primary Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Is Associated with a Specific Intercellular Communication Phenotype
- PMID: 31277464
- PMCID: PMC6678419
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8070970
High Constitutive Cytokine Release by Primary Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Is Associated with a Specific Intercellular Communication Phenotype
Abstract
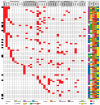
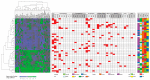
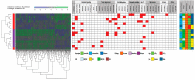
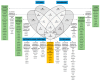
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneous disease, and this heterogeneity includes the capacity of constitutive release of extracellular soluble mediators by AML cells. We investigated whether this capacity is associated with molecular genetic abnormalities, and we compared the proteomic profiles of AML cells with high and low release. AML cells were derived from 71 consecutive patients that showed an expected frequency of cytogenetic and molecular genetic abnormalities. The constitutive extracellular release of 34 soluble mediators (CCL and CXCL chemokines, interleukins, proteases, and protease regulators) was investigated for an unselected subset of 62 patients, and they could be classified into high/intermediate/low release subsets based on their general capacity of constitutive secretion. FLT3-ITD was more frequent among patients with high constitutive mediator release, but our present study showed no additional associations between the capacity of constitutive release and 53 other molecular genetic abnormalities. We compared the proteomic profiles of two contrasting patient subsets showing either generally high or low constitutive release. A network analysis among cells with high release levels demonstrated high expression of intracellular proteins interacting with integrins, RAC1, and SYK signaling. In contrast, cells with low release showed high expression of several transcriptional regulators. We conclude that AML cell capacity of constitutive mediator release is characterized by different expression of potential intracellular therapeutic targets.
Keywords: RAC1; SYK; acute myeloid leukemia; cytokines; differentiation; gene mutations; integrin; proteomic profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Döhner H., Weisdorf D.J., Bloomfield C.D. Acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;373:1136–1152. - PubMed
-
- Arber D.A., Orazi A., Hasserjian R., Thiele J., Borowitz M.J., Le Beau M.M., Bloomfield C.D., Cazzola M., Vardiman J.W. The 2016 revision to the world health organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–2405. - PubMed
-
- Schlenk R.F., Dohner K., Krauter J., Frohling S., Corbacioglu A., Bullinger L., Habdank M., Spath D., Morgan M., Benner A., et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:1909–1918. - PubMed
-
- Valk P.J., Verhaak R.G., Beijen M.A., Erpelinck C.A., Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S., Boer J.M., Beverloo H.B., Moorhouse M.J., van der Spek P.J., Lowenberg B., et al. Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:1617–1628. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

