Modulation of Nitric Oxide Synthases by Oxidized LDLs: Role in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Development
- PMID: 31277498
- PMCID: PMC6651385
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20133294
Modulation of Nitric Oxide Synthases by Oxidized LDLs: Role in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Development
Abstract
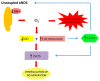
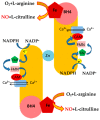
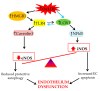
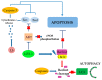
The maintenance of physiological levels of nitric oxide (NO) produced by eNOS represents a key element for vascular endothelial homeostasis. On the other hand, NO overproduction, due to the activation of iNOS under different stress conditions, leads to endothelial dysfunction and, in the late stages, to the development of atherosclerosis. Oxidized LDLs (oxLDLs) represent the major candidates to trigger biomolecular processes accompanying endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation leading to atherosclerosis, though the pathophysiological mechanism still remains to be elucidated. Here, we summarize recent evidence suggesting that oxLDLs produce significant impairment in the modulation of the eNOS/iNOS machinery, downregulating eNOS via the HMGB1-TLR4-Caveolin-1 pathway. On the other hand, increased oxLDLs lead to sustained activation of the scavenger receptor LOX-1 and, subsequently, to NFkB activation, which, in turn, increases iNOS, leading to EC oxidative stress. Finally, these events are associated with reduced protective autophagic response and accelerated apoptotic EC death, which activates atherosclerotic development. Taken together, this information sheds new light on the pathophysiological mechanisms of oxLDL-related impairment of EC functionality and opens new perspectives in atherothrombosis prevention.
Keywords: constitutive NO synthase cNOS; endothelial dysfunction; inducible NO synthase (iNOS); oxidized LDLs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ellagic acid inhibits oxidized LDL-mediated LOX-1 expression, ROS generation, and inflammation in human endothelial cells.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Nov;52(5):1290-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.04.085. Epub 2010 Aug 8. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20692795
-
Foxo1 links hyperglycemia to LDL oxidation and endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells.Diabetes. 2009 Oct;58(10):2344-54. doi: 10.2337/db09-0167. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19584310 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho ameliorates oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced oxidative stress via regulating LOX-1 and PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathways.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Apr 13;16(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0447-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28407763 Free PMC article.
-
Dual signaling evoked by oxidized LDLs in vascular cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 May;106:118-133. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28189852 Review.
-
[Endothelial dysfunction: a global response].Rev Esp Cardiol. 1998;51 Suppl 6:18-22. Rev Esp Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 10050140 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Is Toll-like receptor 4 involved in the severity of COVID-19 pathology in patients with cardiometabolic comorbidities?Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Apr;58:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 32988728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress Triggers Defective Autophagy in Endothelial Cells: Role in Atherothrombosis Development.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;10(3):387. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030387. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The synergistic effect of Citrus bergamia and Cynara cardunculus extracts on vascular inflammation and oxidative stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Tradit Complement Med. 2020 Feb 8;10(3):268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.02.004. eCollection 2020 May. J Tradit Complement Med. 2020. PMID: 32670822 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-35 Mitigates ox-LDL-Induced Proatherogenic Effects via Modulating miRNAs Associated with Coronary Artery Disease (CAD).Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023 Aug;37(4):667-682. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07335-x. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. PMID: 35435604
-
Ethyl Acetate Fraction and Isolated Phenolics Derivatives from Mandevilla moricandiana Identified by UHPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn with Pharmacological Potential for the Improvement of Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 29;13(8):1173. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081173. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maiuolo J., Gliozzi M., Musolino V., Scicchitano M., Carresi C., Scarano F., Bosco F., Nucera S., Ruga S., Zito M.C., et al. The “Frail” Brain Blood Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Early Disruption of Endothelial Cell-to-Cell Connections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:2693. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092693. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lanuti P., Rotta G., Almici C., Avvisati G., Budillon A., Doretto P., Malara N., Marini M., Neva A., Simeone P., et al. Endothelial progenitor cells, defined by the simultaneous surface expression of VEGFR2 and CD133, are not detectable in healthy peripheral and cord blood. Cytom. A. 2016;89:259–270. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22730. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Malara N.M., Trunzo V., Musolino G., Aprigliano S., Rotta G., Macrina L., Limongi T., Gratteri S., di Fabrizio E., Renzulli A., et al. Soluble CD54 induces human endothelial cells ex vivo expansion useful for cardiovascular regeneration and tissue engineering application. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2015;6:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2015.01.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

