Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases
- PMID: 31277663
- PMCID: PMC6610963
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z
Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases
Abstract
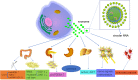
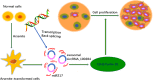
Exosomes have emerged as critical mediators of intercellular communication, both locally and systemically, by regulating a diverse range of biological processes between cells. Circular RNA (circRNA) is a novel member of endogenous noncoding RNAs with widespread distribution and diverse cellular functions. Recently, circular RNAs have been identified for their enrichment and stability in exosomes. In this review, we outline the origin, biogenesis and function of exosomal circRNAs as well as their roles in various diseases. Although their precise roles and mechanisms of gene regulation remain largely elusive, exosomal circRNAs have potential applications as disease biomarkers and novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Biomarker; CircRNA; Exosomal circRNA; Exosome; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Underlying metastasis mechanism and clinical application of exosomal circular RNA in tumors (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Mar;58(3):289-297. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5179. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33650643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles of exosomal circRNAs in diseases.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Jun;23(6):1020-1033. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02485-6. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32935262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal circRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers: Challenges and opportunities.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan 14;17(2):562-573. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.48782. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33613113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and clinical application of exosomal circRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors.J Transl Med. 2022 Apr 5;20(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03367-x. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35382838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal RNAs: Novel Potential Biomarkers for Diseases-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 23;23(5):2461. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052461. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA landscape in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids.Genome Med. 2024 Oct 31;16(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01400-w. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 39482783 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 4;5(9):e699. doi: 10.1002/mco2.699. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39239069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes secreted by Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected colon cancer cells transmit resistance to oxaliplatin and 5-FU by delivering hsa_circ_0004085.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Feb 15;22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02331-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38360615 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-derived circCCAR1 promotes CD8 + T-cell dysfunction and anti-PD1 resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2023 Mar 18;22(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01759-1. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36932387 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal RNAs in the development and treatment of pituitary adenomas.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 17;14:1142494. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1142494. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36875488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boriachek Kseniia, Islam Md. Nazmul, Möller Andreas, Salomon Carlos, Nguyen Nam-Trung, Hossain Md. Shahriar A., Yamauchi Yusuke, Shiddiky Muhammad J. A. Biological Functions and Current Advances in Isolation and Detection Strategies for Exosome Nanovesicles. Small. 2017;14(6):1702153. doi: 10.1002/smll.201702153. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

