Psoralen inhibits malignant proliferation and induces apoptosis through triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress in human SMMC7721 hepatoma cells
- PMID: 31277690
- PMCID: PMC6612100
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-019-0241-8
Psoralen inhibits malignant proliferation and induces apoptosis through triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress in human SMMC7721 hepatoma cells
Abstract
Background: Psoralen is a coumarin-like and coumarin-related benzofuran glycoside, which is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine to treat patients with kidney and spleen-yang deficiency symptom. Psoralen has been reported to show estrogen-like activity, antioxidant activity, osteoblastic proliferation accelerating activity, antitumor effects and antibacterial activity. However, the antitumor mechanism of psoralen is not fully understood. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of psoralen in human hepatoma cell line SMMC7721 and the mechanism of antitumor effects.
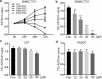
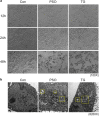
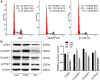
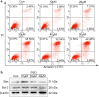
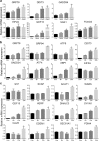
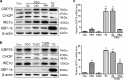
Results: Psoralen inhibited proliferation of SMMC7721 in a dose- and time-dependent manner, and promoted apoptosis. Further, psoralen activated the ER stress signal pathway, including the expansion of endoplasmic reticulum, increasing the mRNA levels of GRP78, DDIT3, ATF4, XBP1, GADD34 and the protein levels of GDF15, GRP78, IRE1α, XBP-1s in a time-dependent manner. Psoralen induces cell cycle arrest at G1 phase by enhancing CyclinD1 and reducing CyclinE1 expression. Moreover, TUDC couldn't inhibit the psoralen-induced ER stress in SMMC7721 cells.
Conclusions: Psoralen can inhibit the proliferation of SMMC7721 cells and induce ER stress response to induce cell apoptosis, suggesting that psoralen may represent a novel therapeutic option for the prevention and treatment hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Psoralen; SMMC7721 cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IMB-6G, a novel N-substituted sophoridinic acid derivative, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis via activation of IRE1α and PERK signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):23860-73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8184. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27009865 Free PMC article.
-
Psoralen inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress in human osteosarcoma cells.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022;60(1):101-109. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2022.0010. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022. PMID: 35257357
-
16-O-caffeoyl-16-hydroxylhexadecanoic acid, a medicinal plant-derived phenylpropanoid, induces apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma cells through ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 1;41:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.01.024. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29519317
-
Human hepatocellular carcinoma: Protection by melatonin.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6486-6508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26586. Epub 2018 Apr 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29672851 Review.
-
[Progress in research of traditional Chinese medicine in inducing differentiation of human hepatoma cells].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2007 Jan;5(1):92-6. doi: 10.3736/jcim20070119. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17214945 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of omaveloxolone in counteracting muscle atrophy post-denervation: a multi-omics approach.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 2;22(1):991. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05810-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39487481 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Antibacterial Activities of Roots and Seeds of Ammi visnaga L. Methanol Extract.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 17;17(1):121. doi: 10.3390/ph17010121. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256954 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the mechanisms underlying the antitumor effects of natural products by targeting the endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 17;14:1293130. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1293130. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38044941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-tumor effect and hepatotoxicity mechanisms of psoralen.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1442700. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1442700. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39161897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psoralea corylifolia L.: a comprehensive review of its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, quality control and pharmacokinetics.Chin Med. 2023 Jan 10;18(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00704-6. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36627680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Gish RG, Porta C, Lazar L, Ruff P, Feld R, Croitoru A, Feun L, Jeziorski K, Leighton J, Gallo J, et al. Phase III randomized controlled trial comparing the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with nolatrexed or doxorubicin. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(21):3069–3075. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–390. - PubMed
-
- Jiang HL, Jin JZ, Wu D, Xu D, Lin GF, Yu H, Ma DY, Liang J. Celastrol exerts synergistic effects with PHA-665752 and inhibits tumor growth of c-Met-deficient hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(7):4203–4209. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

